Enhanced RNA Release from Lipid Nanoparticles with Polymeric Excipients
A novel technology involving the use of acid-responsive polymer additives to enhance RNA transfection from lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemCodelivery of High-Content Ionizable Drugs and Therapeutic Nucleic Acids
High-content drug-RNA nanoparticles formed by replacing the ionizable lipid of conventional LNP platforms for nucleic acid delivery with an ionizable, colloid-forming drug, thereby resulting in novel and high-content drug-RNA nanoparticles.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery System, TherapeuticsMicrofluidic Device and Pump System for Vascularization of Organoids
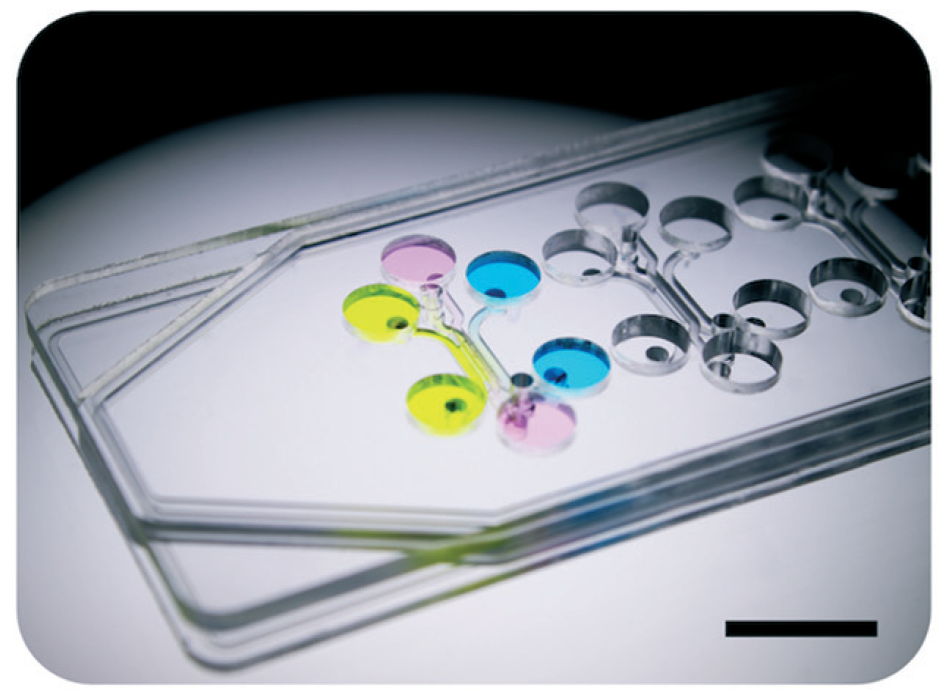
A novel pump-based system for culturing perfusable blood vessels and vascularizing organoids called VIVOS (Vascularized In Vitro Organ Systems). The system consists of an impeller pump connected to a microfluidic device housing a tissue compartment
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsGene replacement therapy for GRIN disorder
Overexpression of GRIN1 as a novel and effective treatment for patients with GRIN1 variants.
Read more...Keywords:
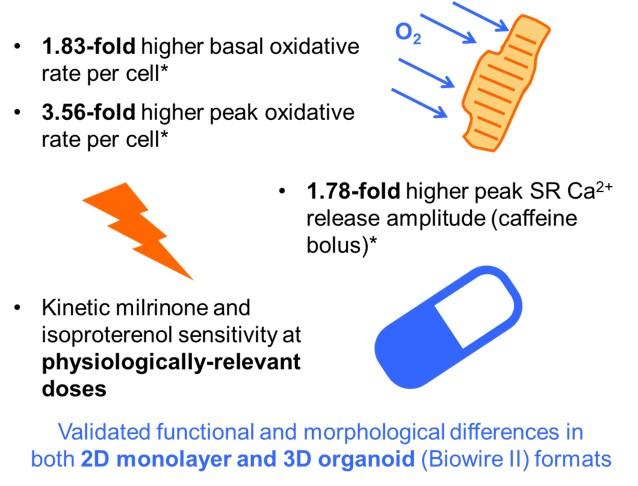
TherapeuticsMaturation Medium for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
A novel and defined culture medium for the functional maturation of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs)
MayoMaxTM Media now commercially available (AxolBio)
- https://axolbio.com/new-myomaxtm-media-enhances-ipsc-derived-cardiomyocyte-maturity-for-superior-in-vitro-cardiac-models/
Keywords:
Research ToolsWireless Earbud for EEG Monitoring and Auditory Stimulation
A compact in-ear device that uses advanced electrodes and ML to monitor brain signals and deliver auditory stimulation in real-time.
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Neurological Disorders, Chips, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Wearable Tech, Advanced Health Technologies, Health & Related Life SciencesLifeAct-GFP RAW264.7 Cells: A Novel Tool for Studying Osteoclastogenesis
A stable Lifeact–mEGFP-transfected RAW264.7 cell line to examine the role of actin filaments in fusion during osteoclastogenesis.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsTherapeutics for TDP-43 Based Neurodegenerative Diseases
A small molecule ‘JRMS’ that harnesses the non-canonical chaperone activity of importin-β1 (Kpnβ1) to prevent and reverse protein aggregation as a therapeutic for ALS and the broader neurodegenerative diseases spectrum.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsFungal-selective Inhibitors of Hsp90
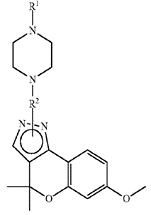
Inhibitors selective against fungal Hsp90. The starting point to design was a lead compound derived from resorcylate macrocycle natural products. A structure-activity relationship (SAR) program was conducted to guide the development of a resorcylate aminopyrazole (RAP) amide scaffold (Figure 1) with high efficacy and selectivity towards C. neoformans and C. albicans Hsp90.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsUltrasound Device for Measurement of Cardiomyocyte Contractility
A ultrasound system capable of detecting cardiomyocyte contractility parameters (i.e. beat rate, beat rhythm, force of contraction) at scales ranging from single cells to 3D microtissue constructs.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsPhosphoproteome Determination using Bioengineered SH2 Domain Superbinders
Researchers at the University of Toronto have proposed a set of cost-effective pTyr enrichment tools (AffiniPure) that can recover a greater percentage of the pTyr-proteome. The technology relies on a set of SH2 domains, which bind pTyr residues, that are bioengineered to be superbinders.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsCost-effective Production of Chitobiose Using Genetically Engineered Bacteria
A cost-effective method for producing chitobiose using genetically modified bacteria. Researchers have used Streptomyces venezuelae, which possesses several secretable chitinolytic enzymes, to extracellularly convert chitin to chitobiose. Key to the invention is the knockout of chitobiose transporter proteins, which severely impairs the ability of the bacterium to import the chitobiose into the cell, leaving the metabolite available for harvesting from the highly enriched culture media.
Read more...Keywords:
ReagentGene Therapy Vectors to Convert Astrocytes to Oligodendrocytes for CNS Diseases
Loss or dysfunction of oligodendrocyte lineage cells (OLCs) is responsible for a number of central nervous system (CNS) diseases or injuries such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injury. In addition, the pathological processes of these diseases are often driven by another resident CNS cell, the astrocyte. Direct lineage reprogramming allows for the generation of new OLCs (tissue regeneration) to be paired with the removal of disease promoting astrocyte (disease modifying mechanism). This two birds with one stone approach may result in more functional recovery for disease and injury than either approach alone.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsPassive Ultra-Broadband Single-Photon Imaging
An optical sensing technology that offers greater sensitivity, bandwidth, and dynamic range than existing sensors.
Read more...Keywords:
Cameras, Computer Hardware, Software, Sensors & Instrumentation, Image & Video ProcessingBiodegradable Neural Electrode for Stimulation, Drug Delivery, and Brain Repair
A temporary, biodegradable brain electrode that can stimulate and deliver drugs to neural cells.
Read more...Keywords:
Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Advanced Health Technologies, Drug Delivery System, Circuit design, Neurological DisordersElectrodeposition coating of calcium polyphosphate for personalized orthopedic implants
Advanced manufacturing to enhance the wear resistance and structural performance of next-gen orthopedic implants.
Read more...Keywords:
Biomaterials, Nanomaterials & Nanoparticles, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Advanced Health TechnologiesNucleic Acid Scaffolded Artificial Immune Complexes for Immune Modulation and Drug Delivery
DNA nanostructures are used to generate synthetic immune complexes that do not exist in nature. The DNA nanostructures provide customizable 3D scaffolds to display antigens in nanoscale spatial patterns, templating the binding of antibodies during immune complex (IC) formation. By tuning the antigen pattern on the DNA nanostructures, researchers are able to program ICs of unique shapes, sizes, and antibody valences, and mediate their delivery to immune cells. The technology can incorporate a variety of therapeutic payloads including protein or peptide antigens, adjuvants, and small molecule drugs, making it a versatile platform for vaccine and immune-modulation and applications.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemA Screening Platform to Identify Protein-Protein Interactions and PPI Inhibitors
Determining and modifying protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are important because their alterations are involved in various diseases. Although numerous techniques are available for studying PPIs, each one is accompanied by various limitations (e.g. high cost, requirement for labeling, inability to recapitulate in vivo conditions, incompatibility with HTS formats and the requirement for highly specialized equipment and expertise). To maximize the capability to explore PPIs, our researchers recently invented Split-Intein Mediated Protein Ligation (SIMPL) where a PPI association event is coupled to intein-mediated ligation. However, the ELISA readout conventionally used with this assay is expensive, time-consuming and cumbersome necessitating an improved detection system.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsCell Line for SARS-CoV-2 Drug Compound Screening
Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a SARS-CoV-2 replicon that achieves three goals: ensures biological safety by mutating genes that are known to be essential for the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to generate infectious viral particles; engineered the replicon in a manner that renders it highly adaptable for high throughput screening facilities; the design ensures full functionality of SARS-CoV-2 molecular replication, polypeptide maturation and organization thus rendering it a high fidelity biologically safe and highly adept tool for screening for inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsGlucose-Responsive Microgels and Microneedle Patch to Prevent Hypoglycemia in Diabetics
This device is a composite transdermal microneedle patch comprising a microneedle array and embedded microgel particles. The microparticles are made from three types of monomers – one provides glucose-responsive volume change, one for stabilizing native glucagon, and one for facilitating glucagon encapsulation. After the microneedle patch is applied, the microneedles penetrate the skin, swell quickly in the interstitial fluid, and enable the microgels in contact with the fluid and glucose. The microgels shrink at low glucose levels squeezing the encapsulated glucagon out, which then diffuses out of the needles to the blood circulation and to the liver thereby increasing blood glucose levels. The entire process automatically proceeds without external intervention of patients or care givers. Using the invented microgel system, the glucagon can maintain native structure and bioactivity at body temperature and under the conditions of making microneedle array.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Medical DevicesVaccines to mobilize B cells for cancer
Our technology is a vaccine that induces patients’ own B cells to produce antibodies that target cancer exclusive peptide MHCI molecules. Specifically, we have developed an antigen design that efficiently delivers a cancer peptide MHCI molecule to the lymph node. This antigen design uniquely triggers the production of peptide MHCI targeting antibodies while traditional antigens (i.e. peptides or whole protein from which the peptides are derived from) fail to do so. Overall, we provide a vaccine platform that induces continuous production of cancer exclusive antibodies directly within patients.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsDeep Learning Performance and Energy Optimization Techniques
This opportunity is a portfolio of hardware and software techniques that seamlessly accelerate AI/ML applications, while saving on-chip and off-chip memory, bandwidth, and processing power. These compute and compression methods have been shown to deliver a 3x boost in processing speed with 2x-4x increase in storage capabilities (up to 10x for natural language processing).
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Chips, Companies, Computer Hardware, Deep Learning, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Smart Cities, SoftwareSerum-free T Cell Expansion Media
Serum-free, T-cell media of comparable expansion potential to serum-based formulations. Using an AI-based, media-optimization algorithm (HiDiNeu) they optimized 14 factors to yield numerous high-performing media formulations.
Read more...Keywords:
ReagentNovel ML for pulmonary function testing on oscillometry devices
Machine learning architecture offers a novel, high-fidelity means of assessing lung physiology during the performance of (monofrequency) oscillometry tests.
Read more...Keywords:
Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Advanced Health Technologies, Diagnostics, Image & Video Processing, Point-of-Care, Biomedical Imaging, SoftwareNovel ML for Pulmonary Embolism Detection
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) diagnosis using machine learning (ML) techniques on CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is transforming the field of medical imaging. PE is a life-threatening condition where blood clots block the pulmonary arteries, requiring timely and accurate detection to improve patient outcomes. Traditional training and development of ML models for PE diagnosis involve extensive annotation, which is resource-intensive. To make these applications practical, the team has developed optimized training strategies, model architectures, and deployment pipelines for efficient PE detection.
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, Biomedical Imaging, Image & Video Processing, Software, Advanced Health Technologies, Point-of-Care, DiagnosticsSmart Traffic Control Software
Machine-learning based methods to improve traffic flow through adaptive signal control.
Read more...Keywords:
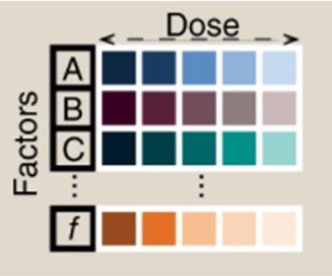
Automotive, Software, Machine Learning, Smart Cities, Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence (AI)Serum-Free Cell Culture Media Design Using an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm
Serum-free cell culture media design is important because it offers the opportunity to construct chemically defined media that possess greater batch-to-batch reproducibility and clinically compatible reagents; benefits not necessarily associated with serum-containing media. As such, it is an ideal method for producing media for the growing cell therapy market segment where high quality and reproducibility standards influence clinical translation. However, the use of defined chemical factors often creates a complex, large-scale optimization problem where the number of possible combinations of factors across different dose concentrations creates a search space so large that only a millionth or less of it can be sampled. Consequently, this renders traditional media optimization techniques ineffective and necessitates the development of new techniques to handle this problem.
Read more...Keywords:
Research Tools, Artificial Intelligence (AI)AI-based cyber threat detection and honeypots
AI-powered cyber threat detection honeypot technologies for ICS, CPS, and IoT that actively engage attackers and draw out more information about their tactics, providing organizations with the intelligence they need to better defend their systems.
Read more...Keywords:
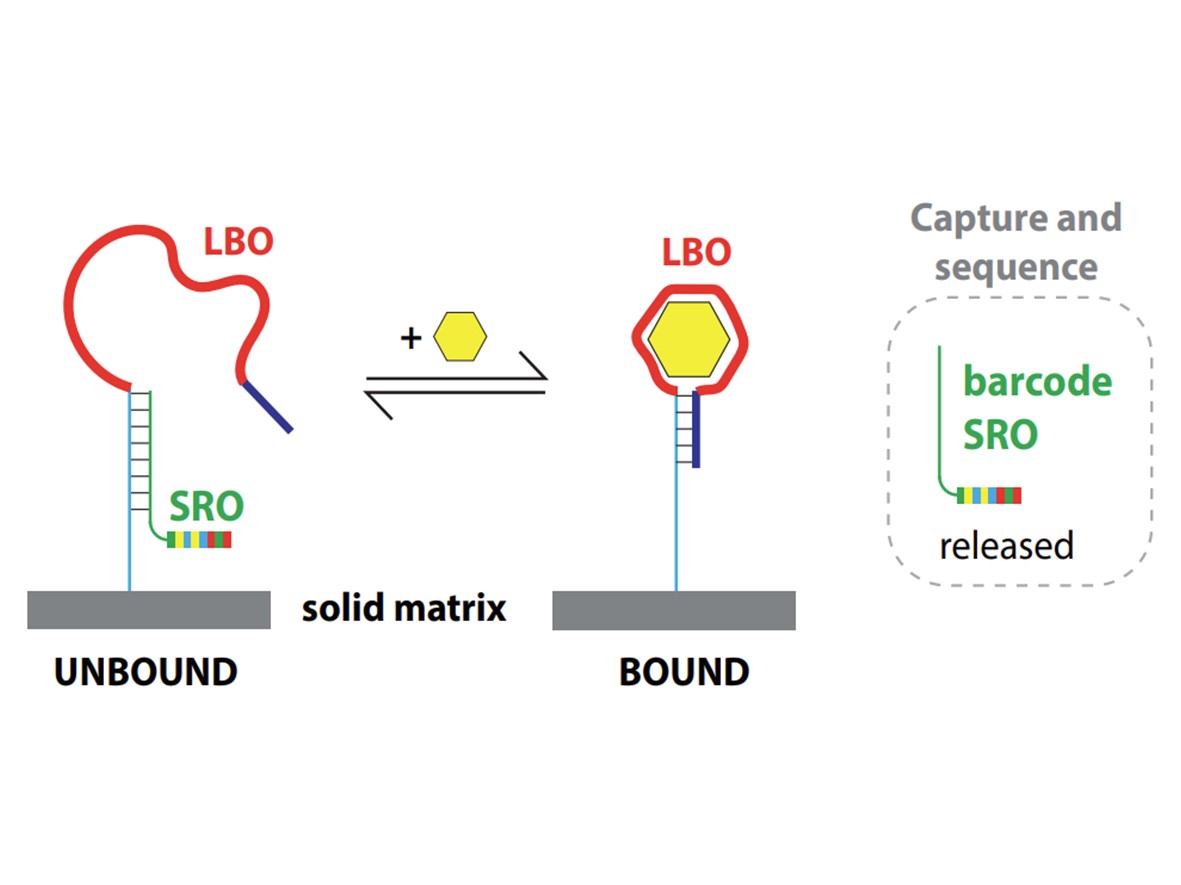
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Energy, Cybersecurity, SoftwareSensitive and Parallel Detection of Small Molecules Using Barcoded Aptamers
Small molecules like metabolites and drugs are at the core of healthcare. The levels of vitamins, hormones, sugars and other critical metabolites gives a snapshot of our health and small molecules like antibiotics, cancer drugs, and antidepressants are vital for treating disease. However, detecting these diverse small molecules is a massive bottleneck in every area of healthcare and medical research. We have developed a new technology that allows us to detect small molecules using DNA sequencing instead of mass spectroscopy. We use small DNA sensors called aptamers to detect each small molecule — different aptamers detect different small molecule targets with high specificity and when any target is detected it gives a unique signal in the form of a DNA sequence readout.
Read more...Keywords:
Diagnostics, Research ToolsEngineered Chondroitinase ABC for Treatment of Traumatic Injury to the CNS
A proteoglycan-rich glial scar forms after traumatic injury to the central nervous system (CNS) and plays a protective role following injury. However, its presence also inhibits long-term axonal regrowth preventing CNS recovery. Chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) is an enzyme that can degrade the constitutive proteoglycans of glial scars, chondroitin sulfate (CS) and dermatan sulfate (DS), and has previously demonstrated therapeutic potential in animal models as large as primates. However, its instability (unfolding, aggregation, and inactivation) at physiological temperature and pH have hindered clinical translation. While repeated bolus injections or constant infusion have been offered as solutions, they suffer from disadvantages like invasiveness and increased risk of infection. Reengineering approaches, while promising, have to date only yielded marginal improvements in stability.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsNUAK Inhibitors as Therapeutics for Cancer and Fibrosis
The Hippo signaling pathway is a key regulator of cell proliferation and cell death. High cell density and stress activate the pathway to stop cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. It has consequently been linked to diseases such as cancer and fibrosis. At the molecular level, the Hippo kinase cassette controls the activity of the transcriptional regulators, YAP and TAZ, through phosphorylation events (Figure 1a). Phosphorylation of YAP and TAZ by a kinase of the Hippo pathway, LATS, results in cytoplasmic localization where these molecules cannot exert their function. However, unphosphorylated YAP and TAZ localize to the nucleus where they can interact with transcription factors (e.g. TEAD) to turn on gene transcription and promote pro-oncogenic, pro-fibrotic outcomes. This implies that molecules that promote TAP and TAZ phosphorylation can act as therapeutics for cancer and fibrosis.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsChimeric Peptide and Delivery System to Prevent Restenosis in Vascular Disease
Balloon angioplasty, usually accompanied with a stent, is used to widen narrowed or obstructed blood vessels in peripheral and coronary arteries. However, restenosis, the re-narrowing of blood vessels, often occurs in patients following the intervention, due to vascular remodelling caused by the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells. Further, there are many peripheral applications where stents not clinically practical. Currently, this pathological remodeling event can be mitigated by introducing the gradual release of either of two classes of drugs (Taxane and Limus) from drug-eluting stents (DESs) and balloons (DEBs). However, these drugs have general cytotoxicity leading to cell death, endothelial dysfunction and late thrombosis.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsBio-based, halogen-free flame-retardant (FR) chemical platform
A synthetic chemistry method that uses vanillin as the starting molecule to yield a novel difunctional phosphorus-containing chemical compound that can be converted into various FR monomeric resins with reactive functionalities.
Read more...Keywords:
Biomaterials, Cleantech, Nanomaterials & NanoparticlesUltralight Aerogels for Extreme Heat Management
Materials and methods for ultra-high heat management in electronics and other critical components
Read more...Keywords:
Electrical & Computer Engineering, Nanomaterials & Nanoparticles, Computer HardwareDynamic, Pixelwise Image Sensing and Systems
This technology includes a suite of inventions, including a fully-functional coded-exposure-pixel (CEP) camera prototype, a novel programmable CMOS sensor, and a method for adaptive adjustment of exposure of every pixel, based on changes in the brightness of the scene for that pixel to extend dynamic range at native sensor resolution.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Cameras, Circuit design, Computer Graphics, Computer Hardware, Software, Image & Video Processing, SemiconductorsPhotodynamic Therapy for Deep Tumors and Tissues
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) can be used to treat a range of non-oncologic conditions as well as a number of solid tumors. It uses light, typically of infrared or visible wavelengths, to activate a localized photosensitizer that results in the selective destruction of unwanted cells. However, an important limitation is the low penetration depth of the employed electromagnetic radiation. Cherenkov light, which is generated when a charged particle passes through a dielectric, offers the possibility of deeper tissue penetration though its low intensity restricts its usefulness in PDT. Researchers at UHN and the University of Toronto have developed a modified version of PDT called Cherenkov-activated Nuclear-targeted Photodynamic Therapy (CHANT-PDT) for the treatment of deep tissues.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsGenetically Encoded Inhibitor to Increase CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing Efficiency
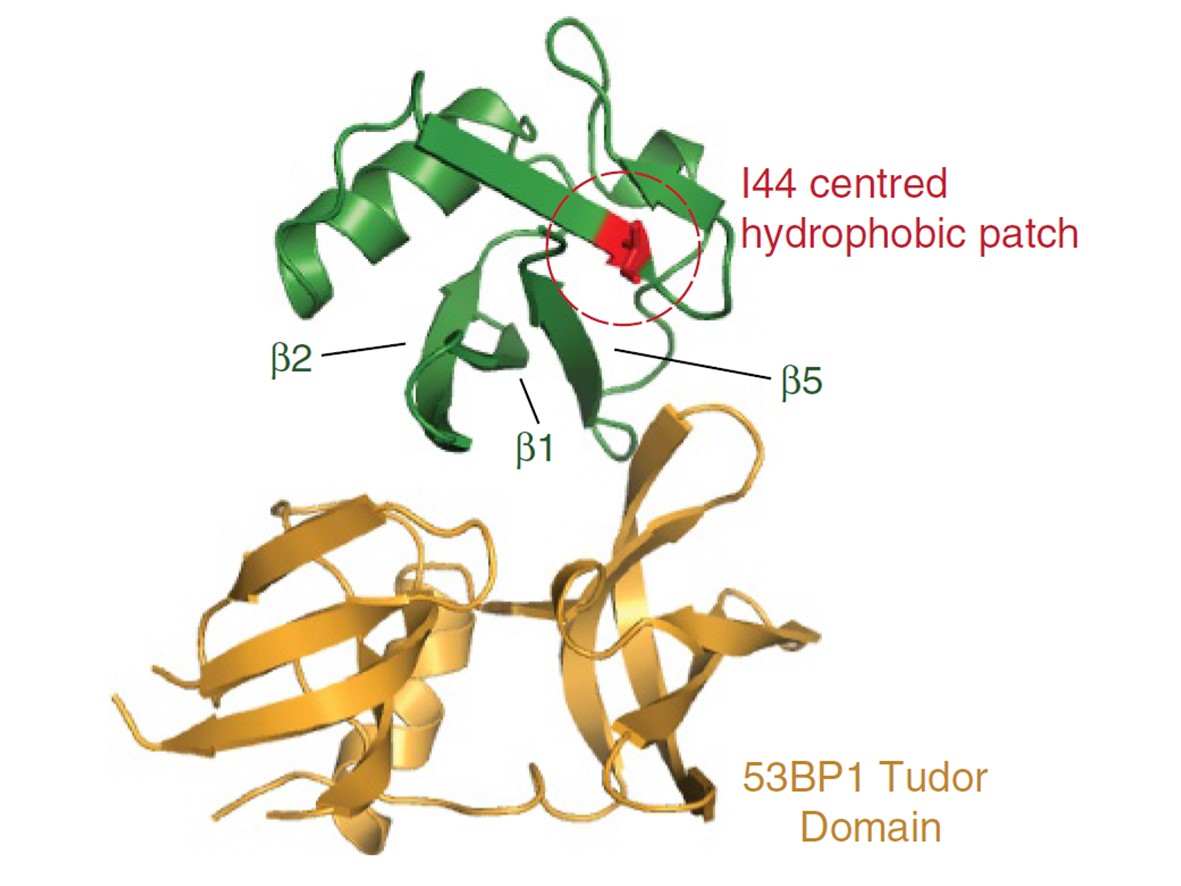
Genome editing with nucleases such as Cas9 relies on homology-dependent repair (HDR) for the targeted insertion or replacement of genetic material. However, as HDR competes with other double-strand break (DSB) repair pathways such as non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), HDR efficiency can often be limiting, posing a challenge to achieving desired levels of genomic alterations. Our researchers have developed a genetically encoded inhibitor of 53BP1 that increases the efficiency of homology-directed repair of DSBs.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsToronto Annotation Suite: AI-Powered Data Annotation
Toronto Annotation Suite (TORAS) is a web-based AI-powered annotation platform.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Automotive, Companies, Computer Graphics, Data Analytics, Deep Learning, Human-Computer Interaction, Image & Video Processing, Neural Networks, SoftwareRapid, remote vital sign monitoring and screening
Based on thermal and optical sensing analysis of digital imaging, this technology allows for rapid measurement of photoplethysmogram (PPG), temperature, respiratory rate, and heart rate beyond conventional distance limitations (e.g. at distances more than 1m), with the ability to add other components (e.g. tissue oxygenation and blood pressure) in the future.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Covid-19, Remote Monitoring, Patient Care, Biomedical Imaging, Software, 3D Imaging, Image & Video ProcessingActive shading devices for eco-efficient buildings
Bio-inspired microfluidic layers for switchable window shading.
Read more...Keywords:
Climate Change, Construction, Microfluidics, Smart CitiesA Low-Voltage Ride-Through (LVRT) Method for Grid-Connected Power Electronic Inverters
This invention enables inverter interfaces of renewable energy sources to generate significantly larger active and reactive currents during LVRT conditions. The increase in the active and reactive powers reaches up to 100% and 15% of the maximum power generated by existing methods, respectively. This would make power systems substantially more resilient during disturbances, reducing the risk of grid instability and blackouts.
Read more...Keywords:
Energy, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Smart CitiesHigh-performance aluminum battery
A next-gen rechargeable aluminum-ion battery technology
Read more...Keywords:
Energy, Battery, CleantechMethod and system for supercritical fluid extraction of metal
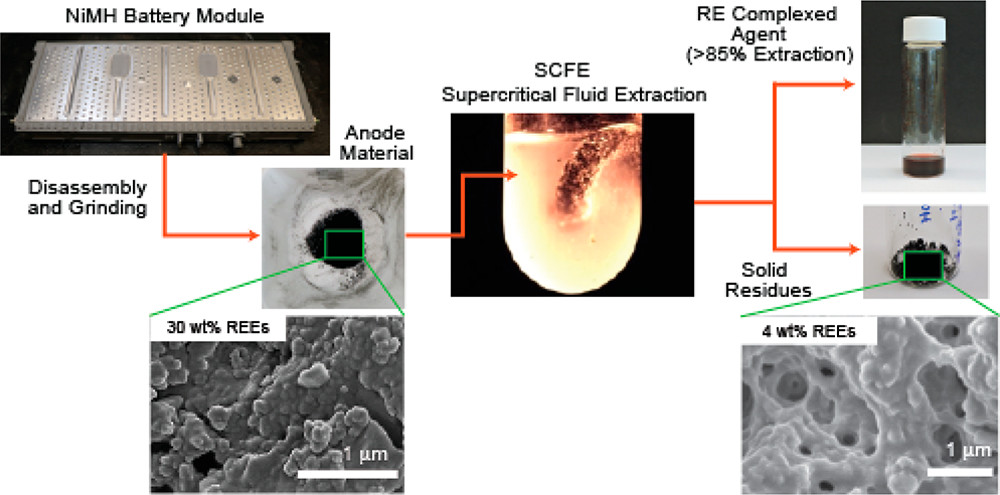
A novel “aerio-metallurgical” process to recycle critical rare earth elements.
Read more...Keywords:
Battery, CleantechRapid, HiFi MRI Data Processing
A DCE-MRI acquisition and reconstruction package that enables more accurate quantification of physiological parameters in larger volumes than any state-of-the-art method. By first performing a high-temporal (rapid), high spatial (hifi) acquisition of anatomical details in the image set, each time frame is reconstructed with a high degree of precision and accuracy.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Biomedical Imaging, MRI, Software, Image & Video ProcessingSiMLQ: Transforming process data into actionable insights
SiMLQ is a process mining solution that uses event data and machine learning to automate the representation, analysis, and optimization of business processes. This enables better allocation of resources, increased productivity, and reduced costs in service systems.
Read more...Keywords:
Data Analytics, Software, Machine LearningCyber-resilient protection for energy grids
Logic for relays that can be used to significantly improve the cyber-resiliency of communication-assisted protection schemes.
Read more...Keywords:
Energy, Cybersecurity, Smart CitiesPrevention of Dental Diseases using Novel Bacterial Peptides
Dental diseases are often caused by a perturbation in the balance of the oral microbiome. Bacterial species that confer positive health benefits may reduce in number shifting the oral composition to more virulent strains and increasing the chance of disease. This harmful shift can be reversed by using commensal bacteria to target and crowd out these pathogens. Researchers at the University of Toronto have isolated a Streptococcus salivarius strain (SALI-10) that can interfere with the growth of periodontal pathogens.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsTwo-stage thermal treatment of nickel sulfide concentrates for nickel extraction
A novel method of Ni extraction that can significantly reduce sulfur dioxide emission, which is a major environmental pollutant.
Read more...Keywords:
CleantechAssay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies
Serological Assay based on split Tripart Nanoluciferase to detect the activity of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, called neu-SATiN, with potential uses towards COVID-19 disease and vaccine management.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsAI-Powered Remote Patient Monitoring Platform
The platform allows for clinical-grade data analysis from wearable sensors (e.g. smartwatches, mobile devices) through proprietary machine learning (ML)-based algorithms that extract clinically relevant data and filter out unreliable sensor data. This platform can provide real-time feedback on patient health, generate more accurate predictions, and enable actionable insights and recommendations to improve care.
Read more...Keywords:
Remote Monitoring, Advanced Health Technologies, Wearable Tech, Health & Related Life Sciences, Software, CompaniesProbiotics to Prevent Dental Cavities
Dental caries (i.e., cavities) occur in 60-90% of school children and nearly 100% of adults. Prevention of this oral disease continues to present serious challenges worldwide. These challenges persist in spite of the fact that caries is known to be a bacterially-mediated process for more than a century. Certain “human-friendly” bacteria which release antimicrobials have the potential to fight diseases caused by pathogenic biofilms. However, probiotics against dental caries have not worked well since many of these probiotic bacteria do not persist in the oral cavity.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsAn Injectable Hydrogel for Delivery of Therapeutics for Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage at the bone joints break down over time. There is no cure for this disease, with one of the first standards of options for disease management being treatments such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, this drug class often has undesirable side effects (e.g. liver and kidney damage) which have been attributed to non-specific systemic delivery. Localized injections directly into the joint space can alleviate these issues, but current methods suffer from reduced retention times. Polymeric solutions can solve this problem, if their other shortcomings such as poor mechanical properties, non degradability, toxicity, poor adhesion, slow gelation and burst release of drugs can be solved.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery System, TherapeuticsAppetite-Suppressing Cytokinin for Weight Loss and Obesity Treatment
Obesity has increased to pandemic levels and is associated with an increased risk of metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease and cancer. While the most effective means to reduce weight is healthy eating and exercise, adherence to these recommendations are a challenge, especially in individuals with a high body weight or BMI >30. Alternatives to these solutions include anti-obesity therapeutics and supplements. Limited therapeutic options are approved by the FDA, such as Glp-1R agonists, but they are restricted to high BMI patients, are costly for insurers/individuals, have limited efficacy or have unpleasant side effects. Similarly, several supplements are available, but none are regarded as being efficacious unless combined with diet and exercise. Consequently, an unmet need in effective weight loss management exists especially for those individuals in the BMI range of 25 – 32 who want to lose a few pounds to avoid the progression towards metabolic disease without altering their current lifestyle.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsCancer Treatment Guidance Using F-box or Cyclin Biomarkers
Targeting of the Wnt pathway is an attractive approach to treatment of multiple cancers as it can play a significant role in carcinogenesis. For example, a first-in-class inhibitor (LGK974) of a protein, porcupine, involved in the Wnt pathway has recently completed Phase 1 safety trials. Inhibition of porcupine prevents the palmitoylation of a Wnt signalling protein, an event that otherwise triggers pro-oncogenic outcomes. However, the beneficial impact of this inhibitor in cancer treatment is negated when inactivating mutations to a downstream tumor suppressor protein, FBXW7, are present in a subset of the population. Such alterations in FBXW7 occur at significant frequencies in patients with uterine, colorectal, cervical, and head and neck cancers. Elucidation of the biomolecular consequences of FBXW7 mutations may lead to suggestive mechanisms to treat these subpopulations.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsGenetically Engineered Proteins for Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
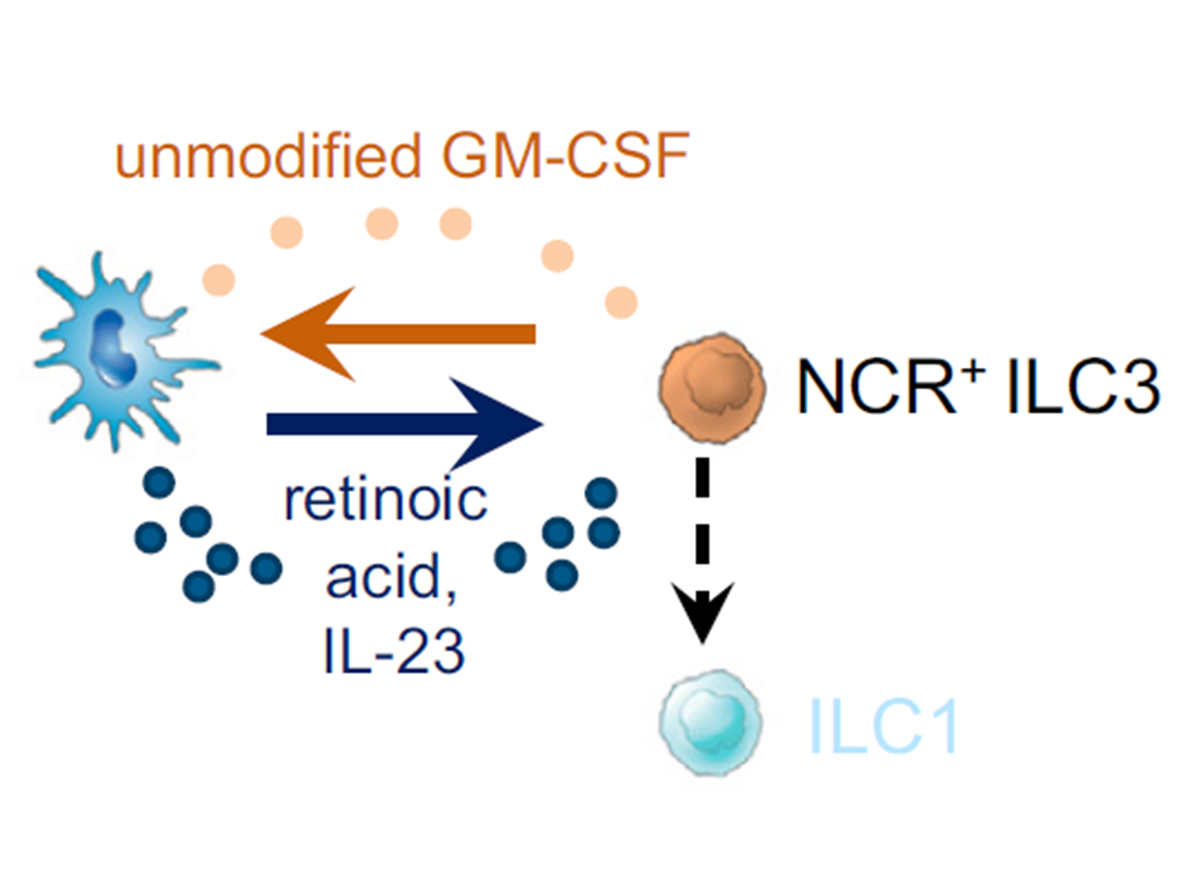
Deregulated balance of the immune system strongly contributes to the development of chronic inflammatory conditions, like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A critical cellular element in sustaining immune and tissue homeostasis are mononuclear phagocytes (MNP), hematopoietic, migratory cells with superior capability to engulf and kill microbes, as well as priming and sustaining adaptive immune responses. Convincing animal research and accumulating evidence in humans suggest that these cells are fundamental in determining whether the immune system is activated or remains tolerant towards microbes. Key to their regulation, particularly in the intestinal tract, is the cytokine Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF). Every 5th patient diagnosed with Crohn’s disease (CD) displays neutralizing autoantibodies (AuABs) against GM-CSF, posing a possible explanation for why previous phase II clinical trials, despite reporting overall improvement of symptoms, failed to reach statistically significant outcomes. If mechanisms to evade these antibodies can be designed, GM-CSF may prove to be an effective treatment against Crohn’s disease.
Read more...Keywords:
Diagnostics, TherapeuticsHi-Efficiency Protection of Linear DNA for Cell Free Protein Synthesis
Cell-free protein synthesis involves the production of proteins in the absence of living cells by using a mixture of extracted machinery and molecular components from chassis organisms (e.g. E. coli). It is an emerging format for the rapid testing of protein properties and function (e.g. functional screening). It is also advantageous in situations where protein synthesis is enhanced by conditions (e.g. pH, redox potentials, temperatures) outside the normal range of cells, and also enables on demand co-and-post-translational modifications of proteins, incorporation of non-natural amino acids, selective and site-specific labelling, and production of toxic or difficult proteins. A key limitation though is the dependence of cell-free systems on plasmid DNA templates which are both timely (>3 days) and costly to generate, reducing the throughput of protein production and slowing the research and development process. A linear DNA template on the other hand can be cheaply and quickly (3 hrs) generated but is susceptible to rapid degradation by exonucleases in cell-free reactions. If this degradation rate could be reduced or eliminated to make cell-free systems compatible with linear DNA templates, the throughput of cell-free protein synthesis could be dramatically increased and production costs sharply reduced.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsAssay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
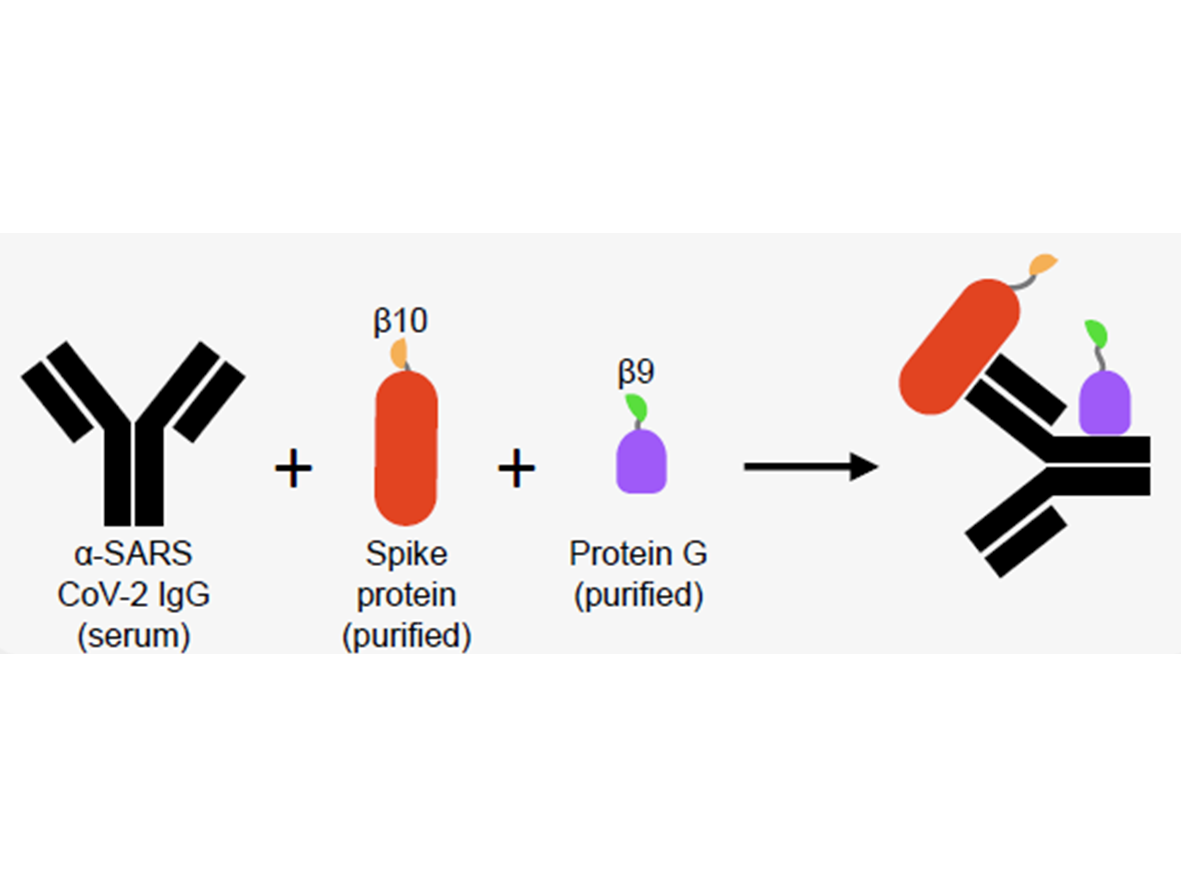
Serological testing is important for understanding the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus by determining how many people in a given population have been infected. The tests are also used to evaluate the responses to current vaccines against this new coronavirus in people who have already been vaccinated. Though several serological tests have been proposed or are in development, the gold standard is still the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). However, this test is time-consuming (~ 6 hrs), tedious (requires multiple washes), and relatively expensive (~$25/test) offering an opportunity to emerging serological tests of comparable quality for probing immune response.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsBoron Containing Bioactive Biomolecules
Boron-containing compounds play an indispensable role in biological and organic chemistry, functioning as intermediates, catalysts and biological probes. The success of several boron-based medicines further emphasizes the potential of incorporating boron into therapeutic agents. Such agents typically contain a considerable number of heteroatoms, thus the development of technologies that introduce boron into these environments are growing in demand.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsSelective Bioactivatable Nematicides for Crops
Plant parasitic nematodes are microscopic worms that impose a severe economic burden on the agricultural industry. To curtail their effects, chemical agents that reduce the fitness of nematodes, called nematicides, have become widespread throughout the world. However, the ecological toxicity and human safety of these chemicals has posed a problem and resulted in bans to some of the most used nematicides. Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed the first bioactivatable nematicides.
Read more...Keywords:
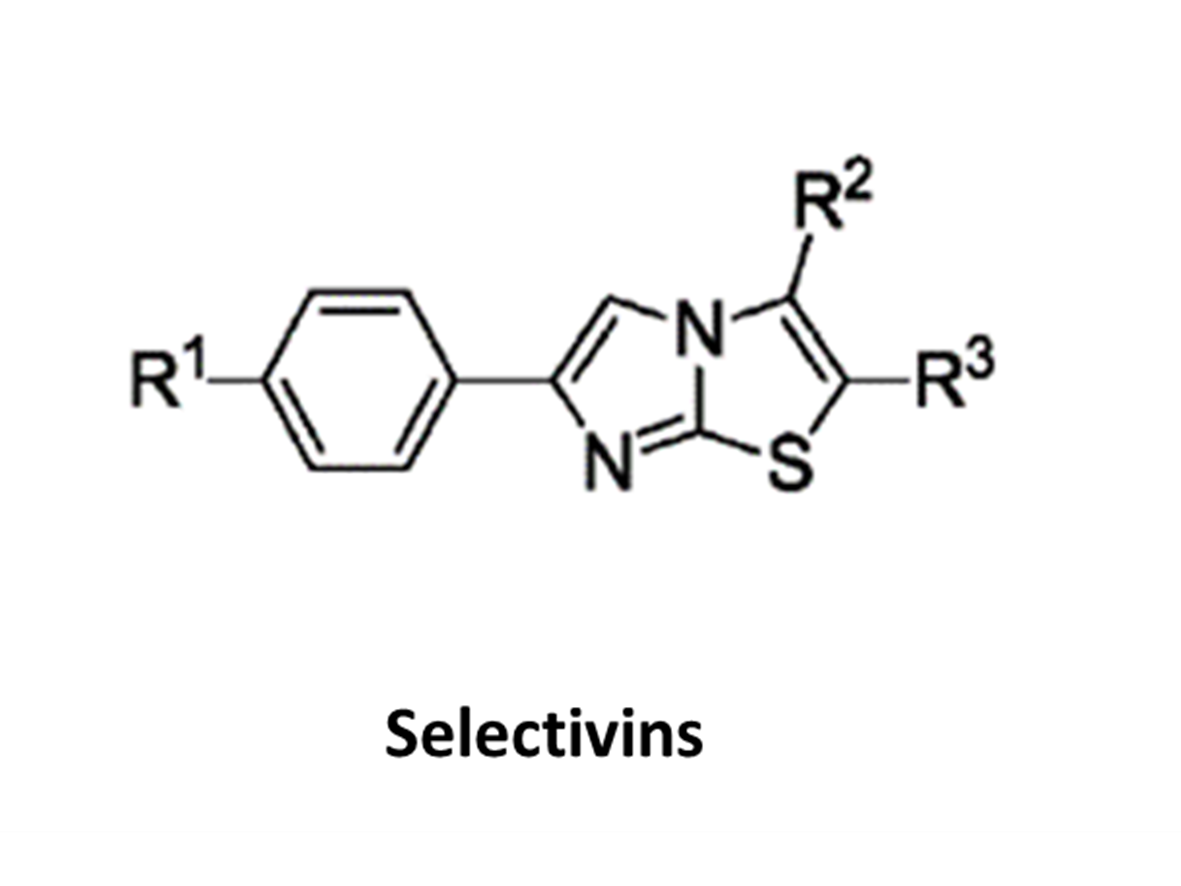
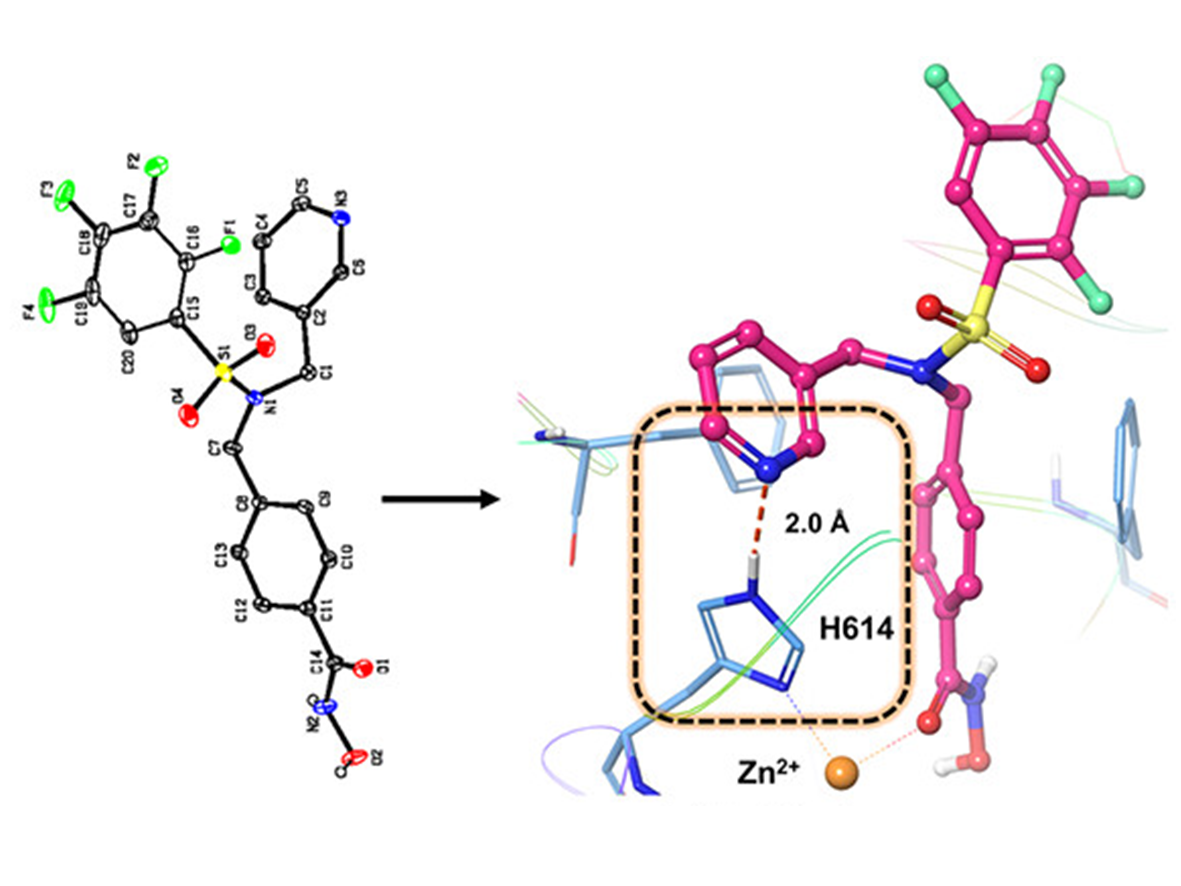
Small MoleculesTherapeutic Targeting of a Novel Gene Product in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), comprising Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic, recurrent mucosal inflammation of the digestive tract. Current treatments come with considerable side effects, are very expensive, and only work in ~50% of patients. Despite recent advances, IBD continues to rise in incidence, burdening our health care system, thereby emphasizing the need to find more effective therapies to treat these diseases.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Small MoleculesSelective HDAC6 Inhibitors for Neurodegenerative Disease
HDAC6 plays an important role in neurological, inflammatory, and other diseases; and thus is an important target for therapeutic intervention. To date, there are no FDA-approved HDAC6-targeting drugs and most pipeline candidates suffer from poor target engagement, inadequate brain penetration, and low tolerability. There are five HDAC6 clinical candidates for the treatment of mostly non-CNS cancers as their pharmacokinetic liabilities exclude them from targeting HDAC6-implicated neurological diseases, urging for the development to address these challenges. They also demonstrate off-target toxicity due to limited selectivity, leading to adverse effects in patients. Selective inhibitors have thus been the focus of development over the past decade, though no selective and potent HDAC6 inhibitor has yet been approved to date.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsFully Homomorphic Encryption
This technology is an optimized version of the Ring-Learning-With-Errors (RLWE) Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) system. This proprietary system maintains encrypted data privacy of communications while still allowing cloud operations to be carried out on the encrypted data, such as Secure Search and Spam-Filter Applications.
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Cybersecurity, Electrical & Computer Engineering, SoftwareResponsive Antiviral Biomaterials
Antibacterial-silica (glass) self-assembled materials that respond to the presence of pathogenic bacteria by releasing drugs on demand when bacteria are present.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemAI-Powered Platform for Better Decision Making
A software platform that leverages statistical inference and machine learning to make more informed decisions.
Read more...Keywords:
Software, Deep Learning, Data Analytics, Computer Graphics, Machine Learning, CompaniesPeptide Therapeutic for Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a disabling and progressive neurological disorder characterized by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons. Current therapies to replace dopamine are only symptomatic and are associated with considerable complications as the disease progresses. No disease-modifying therapies that slow or stop disease progression are available or likely to emerge soon. With Parkinson’s disease affecting over 6 million people worldwide and being the fastest growing neurological disease, this is a huge unmet need in neurodegeneration.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsNanoparticle-based Thermal Contrast Agents
This invention is a unique concept of developing thermal contrast agents to report the detection of a molecule, cells, or tissues. It utilized nanoparticles as probes in hiological and medical detection. The unique aspect of this research is that it did not utilize the colorimetric or fluorescence properties of a nanoparticle as the detection signal but rather, the heat generated from the nanoparticle. This is very unique concept of developing thermal contrast agents to report the detection of a molecule, cells, or tissues.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsMultiplexed Genetic Detection with Isothermal Signal Amplification
This invention describes a diagnostic platform for viral, bacterial, protozoan, fungal and other infections, which allows an exponential amplification of desired nucleic acid molecules at an isothermal condition and simultaneous detection of multiple infectious genetic biomarkers using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) and Quantum Dot (QD) barcodes respectively. Integrating mobile-cellular devices with multiplex molecular diagnostics can potentially provide the most powerful platform for tracking, managing and preventing the transmission of infectious diseases. With over 6.8 billion subscriptions globally, handheld mobile-cellular devices can be programmed 5 to spatially map, temporally track and transmit information on infections over wide geographical space and boundaries. Here we combined recent advances in quantum dot barcode technology with smartphones to engineer a simple and low-cost chip-based wireless multiplex diagnostic device. This device can analyze 20 μL of sample for multiple genetic biomarkers with an analytical sensitivity of 1 – 5 fmol/μL. The addition of an isothermal amplification step enabled the detection of patients infected with HIV and/or hepatitis B from isolated nucleic acid from serum, and identified viral infection in only 1 hour, after blood collection to final read-out. This device advances the capacity for global surveillance of infectious diseases at or near the point-of-care and has the potential to accelerate knowledge exchange-transfer of emerging or exigent disease threats with healthcare and military organizations in real-time.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsA Method to Improve Memory and Mood by Inhibiting Cell-Surface Expression of Alpha 5 Subunit-Containing GABA-A Receptors
This discovery is a unique technique for treating memory and mood disorders. The method is comprised of the administration of a compound that inhibits the protein-protein interaction. These compounds can be used to treat or prevent disorders associated with increased alpha 5 GABA-A receptor function such as memory and mood disorders associated with inflammation or after general anaesthesia.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsMethods for the Prevention and Treatment of Memory Impairment
Over 234 million surgical operations are performed worldwide each year. General anesthetics have dramatically reduced human suffering, but the mechanisms of action of these drugs remain poorly understood. The hippocampus (memory centre in the brain) shelters a population of inhibitory receptors that underlie the memory-blocking properties. GABA (i.e., g-aminobutyric acid) receptors are the most abundant and widely distributed within the central nervous system of mammals. Therefore, these receptors play pivotal roles in virtually all brain functions including memory. Up- and down-regulating the activity of these receptors impairs and improves memory function, respectively. Dr Orser's research aims to understand how anesthetics regulate key inhibitory receptors in the brain. Post-anaesthetic memory loss represents an undesirable and poorly understood adverse effect. Such memory issues after surgery may lead to reduced quality of life, increased admissions to long-term care facilities, premature retirement and death. Modulating the activity of GABA receptors before, during, and/or after the surgery may help patients avoid memory issues, and reduce secondary heath care costs due to general anesthesia.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsUBA5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer and Leishmaniasis
Cancer cells produce and break down proteins more rapidly than normal cells, and are more sensitive to changes in the regulation of processes involving proteins. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is the main protein process that governs protein recycling in cells, and is overactive in many cancers such as leukemia and multiple myeloma. The proteasome is a large protein analogous to the recycling plant of the cell, and inhibition of the UPS with proteasome inhibitors, such as Velcade (bortezomib), results in effective cancer cell death due to the accumulation of undigested proteins. This invention involves the development novel drugs with the aim of making these cancer cells more susceptible to drug treatments, leading to the use of milder drug doses and the prevention or reduced occurrence of drug resistance.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsExcimer-Based Molecular Tool for Detection of Proximally Phosphorylated Protein Sites
Protein phosphorylation is major molecular mechanism through which protein function is regulated in response to extracellular stimuli, it often acts as a switch to proteins' activation and is frequently perturbed in diseases. Currently there are a number of commercialized techniques to detect phospho-proteins, however none of them offers information about the relative spatial arrangement of phosphorylated residues. In biological systems, the extent of phosphorylation of a target is often associated different physiological response and disease state. This invention is the first turn-on fluorescent sensor for the selective detection of proximally phosphorylated protein sites, suitable for application in both aqueous solutions and polyacrylamide gels.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsMammalian Membrane Two-Hybrid (MaMTH) Technology: a Novel Protein Interaction and Drug Discovery Tool
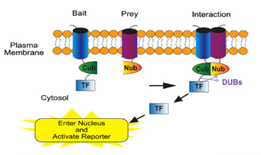
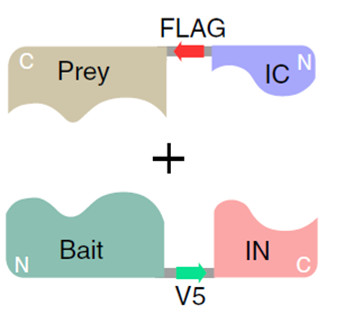
Complex multi-protein clusters play vital roles in many aspects of biology. Deregulation of these clusters may lead to several human diseases including cancer, cystic fibrosis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. This technology uses a bait (protein of interest) - prey (candidate molecules) system to detect and identify novel interacting partners in a mammalian genetic system. Dr Stagljar has built upon his initial patented Membrane Yeast Two-Hybrid (MYTH) invention to propose a unique platform to discover new target molecules for research and drug development purposes. This technology provides a new tool to examine membrane proteins in their natural environment of the human cell. It is sensitive enough to detect minor changes upon the introduction of drugs and thus should prove useful in the development of therapeutics, especially for cancer and neurological diseases.
Read more...Keywords:
Screening Platform, Research ToolsMNAzyme-Based Gold Nanoparticle Sensor
Point-of-care (POC) diagnostics is one of the fastest growing research themes. Simple, cost-effective, and rapid POCs are important to clinicians to make quick and appropriate treatment decisions. This project combines two technologies to create a biosensor that can detect genetic targets, and be further exploited in POC devices. The technology lies on an enzymatic reaction that displays a colorimetric change when specific genetic targets are recognized. This detection strategy is a simple 1- to 2-step assay, low cost, with a better sensitivity than the standard diagnostic technique ELISA. This invention may provide easier and faster POC diagnostics.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsLinker-Based Lecithin Microemulsions as Drug Delivery Vehicles
This invention is a novel formulation for biocompatible microemulsions for use as delivery vehicles for active ingredients in transdermal, topical and oral delivery. The formulation is based on five basic ingredients: lecithin (extracted from soybean or other source); a lipophilic additive such as long change alcohol or long chain fatty acid, monoglyceride, or sorbitol ester; a hydrophilic additive containing C6-C9 fatty acids partially saponified; a C8-C20 fatty acid ester; and water. Particular combinations of these ingredients, at specific ratios, yield thermodynamically stable microemulsions capable of increasing the solubility (in isotonic solutions) of hydrophobic drugs such as lidocaine, and alpha-tocopherol acetate by more than 20 fold.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemRe-PAIR: A CRISPR-Based Technology for Portable Diagnostics & Biotechnology
Our scientists have engineered a new nucleic acid sensor, based on CRISPR technology, that is cell-free and can be rationally designed for broad applications in portable diagnostics, in sensing and in biotechnology. This novel, portable nucleic acid sensing platform uses a CRISPR technology that, unlike previous technologies, can be deployed outside of the lab without pre-packaged RNA inputs, and can generate multiplexed signals in any reporter mode (e.g. colorimetric, electrochemical, enzymatic, fluorescent). The flexibility afforded by this platform will allow for the sensitivity, resolution and programmability associated with other CRISPR-based diagnostics, but resolves the practical challenges related to their implementation.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsNanoparticles to Enhance Anti-Bacterial Properties and Integrity of Dental Tissue in Root Canal Treatment
Our researchers have developed a novel method that uses proprietary composition of stabilized multifunctional nanoparticles in combination with photodynamic activation to obtain durable and more effective endodontic treatments (root canal therapy). The use of a natural biopolymer allows a better integration into the dentin host tissue, and the production of anti-microbial activity similar to natural dentin. The biopolymer nanoparticles conjugated with photosensitizers have the dual effect of increasing anti-biofilm efficacy and minimizing toxicity compared with standard root canal filling materials. The combination of engineered nanoparticles and photo-activation will destroy remnant microbes and promote a natural mineralization of treated teeth, thus reinforcing the hard tissue dentin while limiting bacterial entrance.
Read more...Keywords:
BiomaterialsCRISPR-Based Screening Platform Technology for Drug Discovery
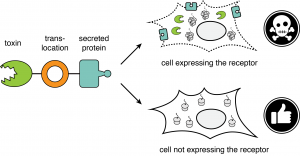
This technology relates to a novel method to discover receptors for extracellular proteins in an unbiased fashion. The approach is based on a simple concept: bacterial exotoxin, when fused to a secreted protein, intoxicates cells in a receptor-dependent manner, which facilitates the identification of the cognate receptor through genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9-based positive selection screen.
Read more...Keywords:
Screening Platform, Research ToolsD-PHI: Elastomers for Use with Protein Based Media
Tissue-material interactions govern the efficacy of biomedical devices implanted in the body. Protein adsorption that occurs on a biomaterial surface influences cell action on those surfaces in vitro and in vivo, including but not limited to the innate immune response cells (neutrophils ,monocytes and macrophages) which are essential in driving the body's early response to a b1omaterial, and other cells such as endothelial cells, fibroblast, smooth muscle cells, stem cells, etc. There is a need for elastomeric materials in the biomaterials field which are degradable and have an ability to interact with proteins in a manner that favors wound healing. A novel finding of this invention was the observation that specific formulations of a degradable, polar hydrophobic ionic polyurethane (0-PHI) system synthesized by Santerre et al. has demonstrated good biocompatibility by means of protein adsorption related to immunoglobulin proteins and specifically immunoglobulin G (lgG). This will have applications for the use of biomaterials in sensors, implant scaffolds, tissue repair fillers and numerous other blood and tissue contacting devices.
Read more...Keywords:
Biomaterials, Drug Delivery SystemHuman Culture Assay to Assess Muscle Stem Cell Potency
Our researchers have developed an in vitro stem cell mediated skeletal muscle repair platform referred to as “MEndR” (Muscle Endogenous Repair), that accurately recapitulates the timing of key phases of the stem cell (SC) mediated skeletal muscle repair process in a dish (SC-expansion, SC cell cycle exit, SC nascent fiber formation, fiber maturation). Furthermore, this in vitro platform accurately predicts the performance of stem cells at mediating in vivo repair in standard in vivo mouse transplantation assays and has the potential for parallel stratification of the potency of many (100s) drug or cell therapy candidates at enhancing muscle regeneration.
Read more...Keywords:
Diagnostics, Research ToolsNovel Substrates for Chemically Defined Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells
Our researchers have developed a novel culture substrate combination that robustly supports human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) proliferation and pluripotency in chemically defined conditions. hPSCs grown on this novel substrate culture display higher proliferation rates and pluripotency marker expression than current gold-standard culture substrates Geltrex- and vitronectin-coated plastic. Because this invention uses human recombinant proteins in combination with chemically defined media, it addresses the unmet need for defined culture platforms (culture substrate and media) required to generate clinical-grade cells for future cell therapy and broader medical applications. Furthermore, these substrates provide additional benefit to basic research through avoiding lot-to-lot variation and potential confounding effects associated with using undefined matrices (Geltrex and Matrigel).
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsIntegrated Quantum Dot Barcode Smartphone Optical Device for Diagnostics
The focus of this technology has been to develop an automated portable device that can extract, amplify, detect, & database the results. This was made possible by the use of innovative engineering approach to assemble each function into a disposable cartridge system. This cartridge system also contains tablets of reagents with known concentrations, so that the device can be portable without the need for refrigeration or unique storage. The detection is then identified by a smartphone camera & databased on a software App.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsIntegrated Quantum Dot Barcode Smartphone Optical Device for Diagnosis of COVID-19
The focus of this technology has been to develop a versatile diagnostic system by using quantum dot barcoding technology in combination with the engineering of a detecting and processing device. This device is proposed to extract, amplify, detect, and database the results, which has been made achievable by the use of innovative engineering approach to assemble each function into a disposable cartridge system. The cartridge system also contains tablets of reagents with known concentrations, so that the device can be portable without the need for refrigeration or unique storage. The detection is then identified by a smartphone camera and databased on an software App.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsInhibition of PKN1 As Therapy For Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Our researchers have developed a new strategy to overcome the drug resistance often faced during the treatment of CLL by inhibiting the TNFR family signalling through inhibition of a kinase, PKN1, which is involved in TRAF1 regulation. TRAF1 is overexpressed in 48% of B cell related cancers with highest expression in mature B cell lymphomas and the most refractory B-CLL. Thus targeting TRAF1 in human CLL has the potential to improve the disease outcome. Non-coding single nucleotide polymorphisms in TRAF1 have also been linked to non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. They have identified PKN1 inhibitors and shown in proof of principal studies that inhibiting PKN1 lowers TRAF1 levels and survival of CLL cells. They have also successfully tested & shown that the PKN1 inhibitors can work in synergy with standard of care drug as further validation for PKN1 as a target in CLL.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsRecombinant Antibodies Network (RAN)
The Recombinant Antibody Network (RAN) is a multi-institutional research consortium (member institutions: The University of Toronto, University of California San Francisco and The University of Chicago) created accelerate the identification and development of recombinant antibodies raised against valuable and challenging targets to support drug development and cutting edge biomedical research. The RAN was founded by three ex-Genentech antibody engineers. To date the team has screened and validated over 880 antibodies, some of which are now available for licensing as therapeutics.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Diagnostics, Research ToolsImmunotyping COVID-19 Patients Using Novel Protein Complementation-Based Assay
Motivated by the current urgency due to the pandemic, University of Toronto researchers (with extensive expertise in protein engineering) are developing a set of novel immunoassays for detecting anti-CoV-2 antibodies (IgM and IgG) directly in patients sera based on protein complementation assay (PCA), specifically on tri-part split NanoLuc. For this, they are repurposing their recently developed and patented Split Intein-Mediated Protein Ligation (SIMPL) (1) detection assay to develop an innovative diagnostic immunoassay for detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 Abs directly from COVID-19 patient sera by adapting the tri-part split NanoLuc assay.
Read more...Keywords:
Research Tools, Screening PlatformThe Glucose Meter as a Detection System for Point-of-Care Gene Circuit Diagnostics
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on fluorescent reporter proteins which require multi-well plate reader assays, leaving the technology for all practical purposes stuck in the laboratory. In line with this promise of cell free gene-circuit sensors, we have developed a cheap and accessible detection method at the University of Toronto.
Read more...Keywords:
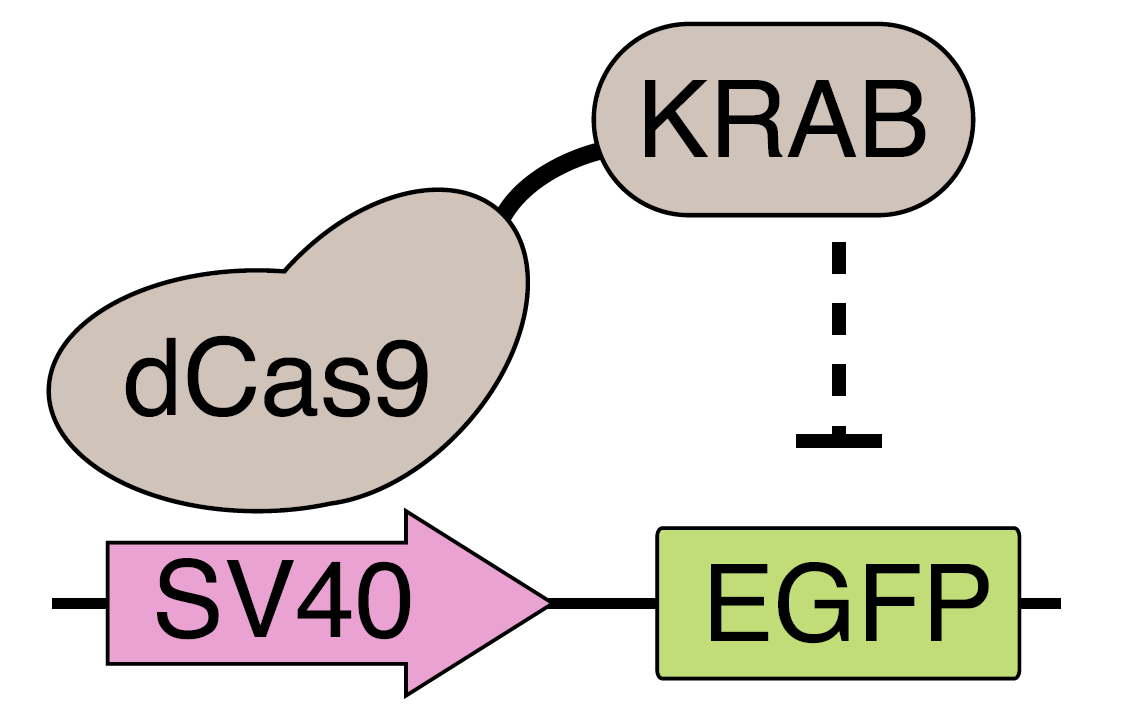
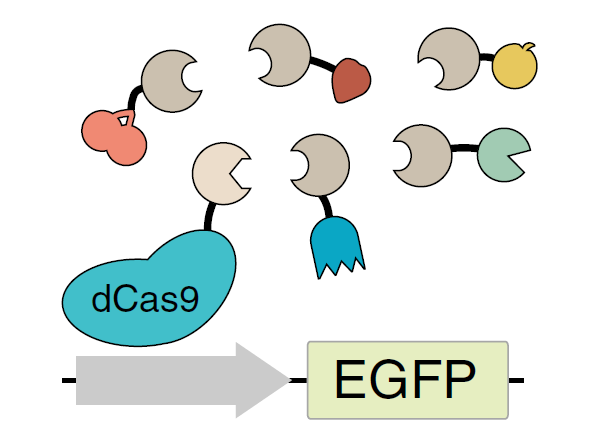
DiagnosticsProtein Domains for Controlling Gene Expression
Precisely controlled regulation of gene expression in cells, tissues, and organisms is one of the major challenges in tissue engineering, cell-based therapies, and gene therapy. Controlled gene expression in cells is achieved either by exogenously introducing cDNAs by transfection or viral transduction, or by introducing sequence-specific transcriptional regulators. These regulators include zinc-finger nucleases, transcription activator like effectors (TALEs), or enzymatically inactive Cas9 (dCas9) which are fused to transcriptional activation or repression domains to achieve the desired effect on gene expression. Of these techniques, CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) based on the fusion of inactive Cas9 (dCas9) to the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) repressor, is a powerful platform for silencing gene expression. However, it suffers from incomplete silencing of target genes.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Research ToolsMicro-robotic Capsule for Drug Delivery and Microbiome Sampling
Access to a patient’s GI tract, either for purposes of delivery of therapeutic agents or collecting samples for diagnostic purposes faces a number of challenges. For the former, oral administration, requiring transit through the stomach and upper GI, can impact the stability and solubility of therapeutic agents such as antibodies or probiotics. For the latter, current procedures for retrieving microbiome samples rely on the use of highly invasive endoscopic procedures. Consequently, many diagnoses of gut health (for example to monitor diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or cancer) rely on analysis of a patient’s stool, material that does not reflect the conditions that occur higher up in the GI tract. There is therefore an urgent need for both drug delivery and collection (GI sampling) systems for more effective and precise disease intervention.
Read more...Keywords:
Diagnostics, Research ToolsNanoconstructs for Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia affecting ∼ 5.8 million Americans and 40-50 million people worldwide. Despite the burden of this disease, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s with standard-of-care treatments only able to manage symptoms. Furthermore, clinical diagnosis is imprecise and only suitable for later stages of the disease as it relies on detecting impaired memory and cognitive function, which consequently also results in late intervention. However, changes in neurological biomarkers precede cognitive decline by 15 – 20 years and can thus act as indicators of Alzheimer’s disease enabling early diagnosis and clinical intervention. Though several techniques such as cerebrospinal fluid sampling and various medical imaging methods have demonstrated promise in this regard, none of these have progressed to routine use.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, DiagnosticsAn Improved CRISPR-Cas System for Systemic and Combinatorial Genome Wide Screens
Genome wide knockout screens can be used to elucidate genetic pathways and identify novel drug targets. They work by analyzing the impact of gene inactivation on a measured physiological readout, such as cell survival. CRISPR-Cas9 is a simple and effective tool used to disrupt single genes on a large scale. However, generating the necessary pooled libraries to simultaneously inactivate two or more genes (i.e. double knockout) is challenging. Furthermore, other limitations that impact its efficiency exist, such as recombination between duplicated promoters and expression cassettes. Cas12a has been proposed as an attractive alternative to Cas9 as its intrinsic RNAase activity can be used to generate multiple distinct gRNAs from a single concatemer. However, it too has its deficiencies, such as a low double knockout efficiency (15%). Thus, there is a need for improved techniques to probe genetic interactions (GIs) between two or more gene participants.
Read more...Keywords:
Research ToolsDetection of Pathogens using Electrochemical Sensing
Pathogen detection is important to such applications like environmental monitoring, clinical diagnostics and biological agent recognition. Most detection methods are very specific and focus on identifying the particular strain of bacteria or virus. However, in applications such as lake or drinking water testing the general monitoring of overall pathogenic load may be better suited to identifying a contaminated water source and preventing sickness. To this end, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes and recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs), may serve as general, broad-spectrum identifiers of pathogenic presence or load when detected in important environmental samples.
Read more...Keywords:
Sensors & InstrumentationA Drug Delivery Method to Increase Delivery of Nanoparticles to Cancer Tumours
The delivery of nanoparticles into solid tumours is critical to their utility for diagnosing and treating cancer. Yet only 0.7% of nanoparticles successfully localize to solid tumours largely due to clearance by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), resulting in poor clinical translation of nanomedicines. Though various solutions have been proposed; modifying various physicochemical properties of nanoparticles such as size, shape, and surface chemistry, or using biological techniques such as ablating or saturating Kupffer cells, these have only resulted in minor increases in delivery. Furthermore, another challenge is that none of these approaches present a central and systematic principle for improving delivery efficiency.
Read more...Keywords:
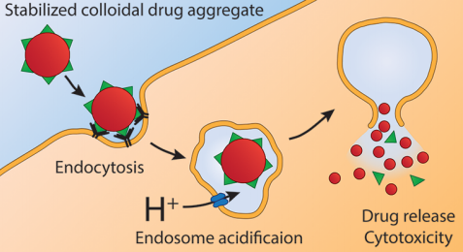
Drug Delivery SystempH-Responsive Colloids for Enhanced Drug Delivery
The aggregation of small molecule drug candidates to form larger colloidal structures can render a promising drug ineffective. This limited efficacy is due to the inability of colloids to directly cross the plasma membrane due to large size (100 – 1000 nm). Furthermore, while strategies enabling uptake of colloids by cells exist, they are often still trapped within the endo-lysosomal pathway that isolates them from the main cell body. Despite this, the very high drug content of colloids (> 50%) renders them as ideal drug delivery systems if the propensity of their monomeric small molecule subunits to aggregate can be triggered towards dispersion, or drug release.
Read more...Keywords:
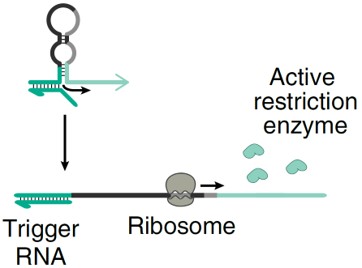
Drug Delivery SystemPoint-of-Care Detection of Infectious Disease Using Restriction-Enzyme-Based Reporters
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on optical reporter proteins which require equipment contained in centralized labs and which offer limited multiplexing capabilities. To overcome these limitations, researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a direct gene-circuit/electrode interface that allows point-of-care detection of RNA.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsMicrofluidic Platform for Uniform Spheroid Growth, Release, and Drug Screening
Spheroids and organoids have been proposed as alternative systems to animal models for testing of compounds for the pharmaceutical or personal care products industry. Some of the advantages they offer are cost and time savings, reduced ethical issues, and potentially more faithful reflections of compound response in humans. However, their broad scale adoption requires consistent reproducibility across spheroid-to-spheroid and batch-to-batch when multiplexing and a high fidelity in structural and functional biomimicry. Limitations in these areas would otherwise mask the treatment of a drug and is thus particular problematic in compound screening applications. Furthermore, a more biologically reflective method to control spheroid/organoid matrix stiffness would also be useful in modelling diseases where the matrix plays a key role (e.g. cancer and fibrosis), and the capability for high-throughput screening would also be advantageous.
Read more...Keywords:
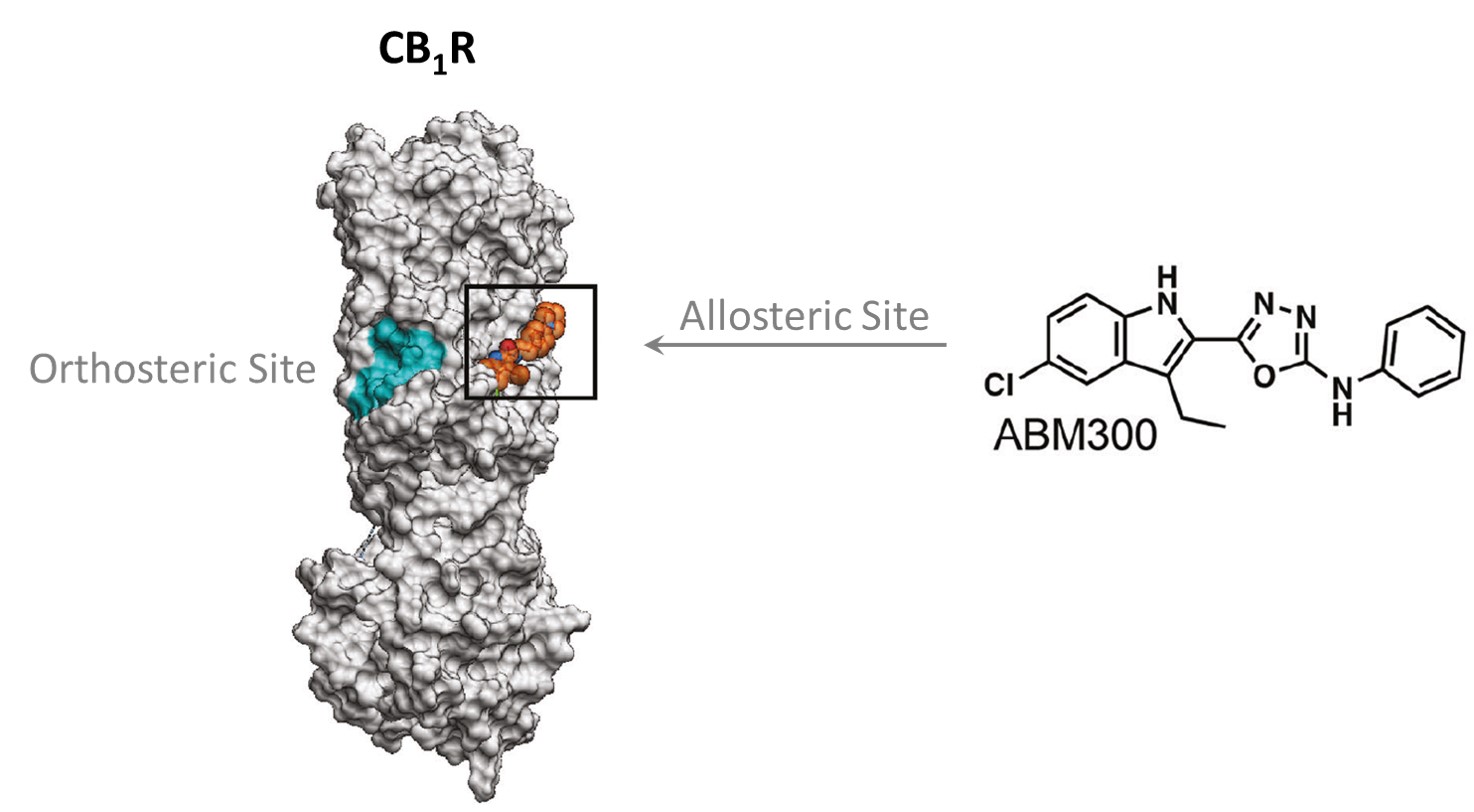
Organ-on-a-chipA Small Molecule Allosteric Modulator of CB1R for Treatment of Psychosis and Schizophrenia
Psychosis and schizophrenia are associated with dysregulation of multiple neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, serotonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and glutamate. Treatments for these disorders rely on the use of antipsychotics which target several G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) such as those for dopamine and serotonin. However, these therapeutics are associated with a range of side effects including extrapyramidal motion, sedation, metabolic syndrome, and weight gain. The ability of the endocannabinoid system, including the cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1R), to modulate dopamine neuron signalling offers a route to indirectly correct for the hyperdopaminergic underpinnings of these disorders while possibly avoiding the negative side effects of current antipsychotics. As efforts to target CB1R at the orthosteric site have not yielded beneficial clinical outcomes, allosteric modulation may offer an alternative pathway.
Read more...Keywords:
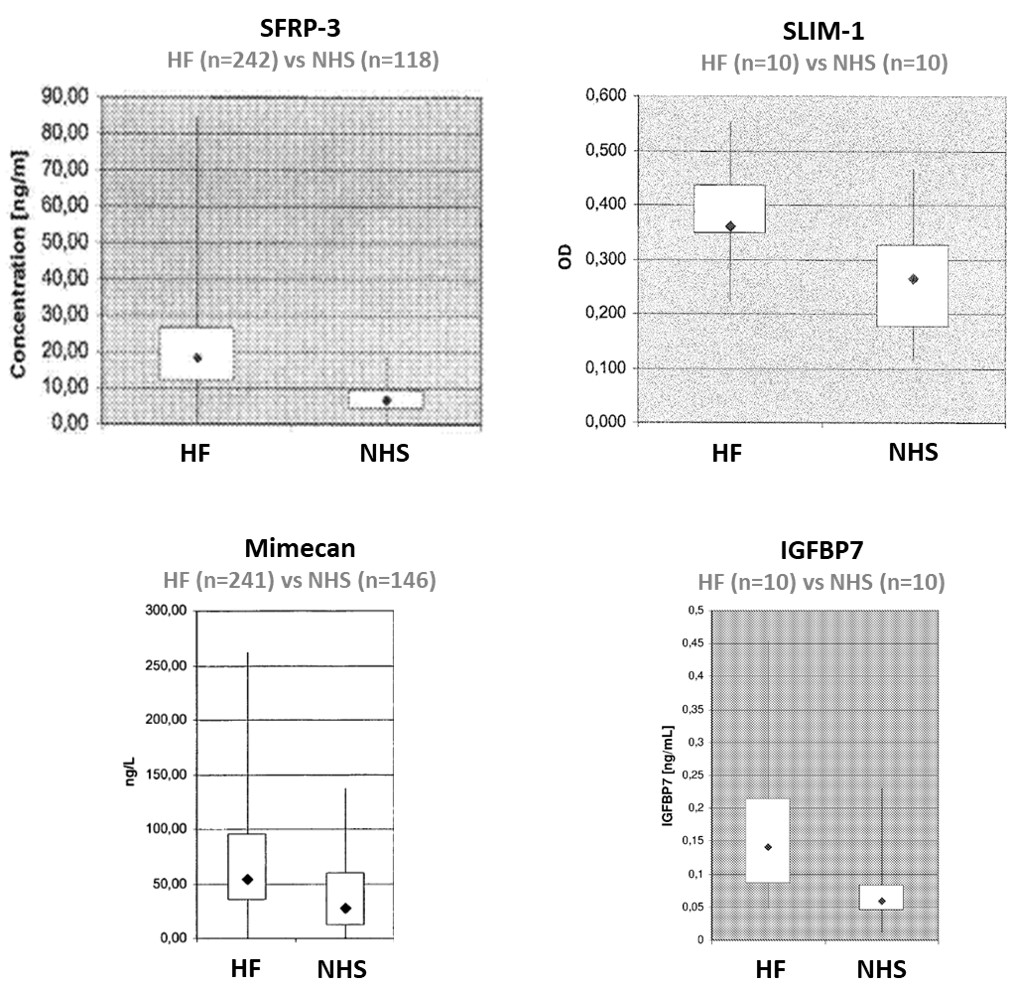
TherapeuticsBiomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF) is one of the most prevalent, costly and life-threatening diseases in developed countries. Early diagnosis of this disease is a challenge as decline in the cardiac output does not occur until the later stages of HF due to certain compensatory mechanisms. Thus, biomarkers are useful in supplementing information from the detection of physical or structural abnormalities by various techniques (e.g. echocardiogram). Natriuretic peptides (particularly NT-proBNP), cardiac troponin, and markers of inflammation are all used in the clinic, though none of them is diagnostic with 100% specificity and 100% sensitivity. New biomarkers, individually or in a panel, can thus improve the current standard of diagnosis or prognosis of HF.
Read more...Keywords:
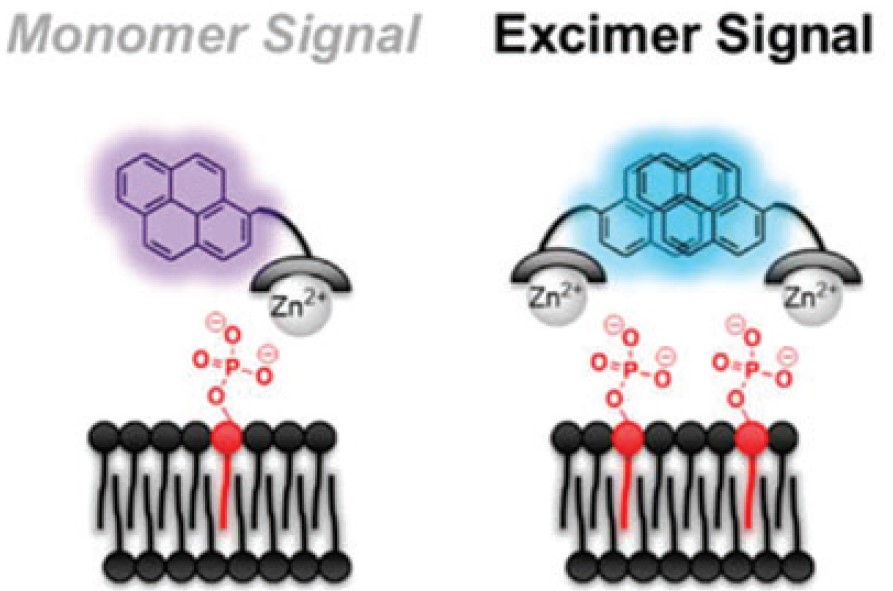
DiagnosticsChemosensors for Detection of Bacteria, Apoptosis, and Phospholipidosis
Detection of negatively charged phospholipids can serve as indicators of apoptosis, bacterial presence, or diseases such as phospholipidosis. For example, phosphoserine, a negatively charged lipid, is largely present in the outer membrane of mammalian cells only in the event of apoptosis, while the negative net charge of bacterial membranes can serve to differentiate these cells from mammalian ones. Consequently, the phosphoserine binding protein, AnnexinV, has been used for detection of apoptosis, while the small molecule Zn2+-containing fluorophore, PSVueTM380, has been used for generic detection of negatively charged phospholipids and their indicative states. However, AnnexinV has several limitations (high Ca2+ levels required for binding, biochemical instability, slow rate of binding, need for washes) and the turn-on sensor PSVueTM380 has a short dynamic range.
Read more...Keywords:
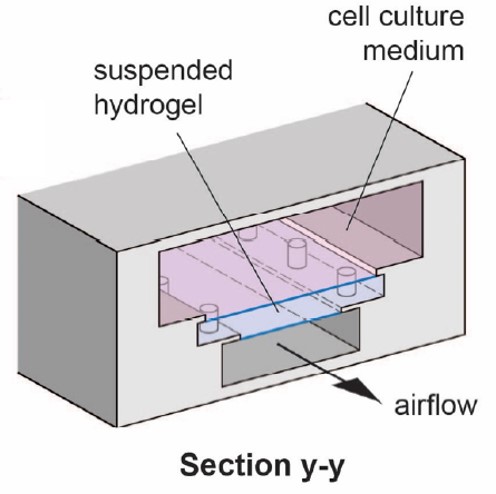
Research ToolsOrgan-on-a-Chip for Airway Tissue Modelling
Lung-on-a-chip microfluidic devices offer the promise to revolutionize the study of disease and the pre-clinical testing of drug compounds, as they possess several advantages over animal models. However, recapitulating the lung architecture is challenging and most current devices only capture certain anatomical features, such as the lung alveoli in Emulate’s commercially available “breathing” alveolus-on-a-chip device. In the latter device, cells are grown on elastomeric material that (i) does not recapitulate the extracellular matrix and (ii) is more importantly not readily amenable to the off-chip analytical techniques (e.g. immunohistochemistry, PCR, histology sectioning) often used to ascertain perturbing changes in animal tissue.
Read more...Keywords:
Organ-on-a-chipTargeted Protein Degradation using Novel E3 Ligases
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is an alternative approach to conventional paradigms (e.g. small molecule inhibitors) that target disease. In this technique, a PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) or a molecular glue is used to initiate the degradation process of the targeted protein. While these two molecular classes are mechanistically distinct, they both enable degradation by recruiting an E3 ligase, an enzyme which enables the transfer of the ubiquitin tag needed for proteasome-mediated degradation. One obstacle to the development of these treatment modalities is that the two E3 ligases largely used with this approach only work with some proteins. Thus, identification of new E3 ligases can increase the disease targeting space of targeted protein degradation therapeutics.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Research ToolsTunable Activation of Gene Expression for Therapeutic Use
Precisely controlled regulation of gene expression in cells, tissues, and organisms is one of the major challenges in tissue engineering, cell-based therapies, and gene therapy. Controlled gene expression in cells is achieved either by exogenously introducing cDNAs by transfection or viral transduction, or by introducing sequence-specific transcriptional regulators. These regulators include zinc-finger nucleases, transcription activator like effectors (TALEs), or enzymatically inactive Cas9 (dCas9) which are fused to transcriptional activation or repression domains to achieve the desired effect on gene expression. Of these techniques, CRISPR activation (CRISPRa), based on the fusion of inactive Cas9 (dCas9) to various trans-activation domains, is a powerful platform for activating gene expression. However, non-human activators (e.g. VP16) can elicit an immune response necessitating the development of human activators of comparable and tunable efficacy.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Research ToolsAgonists for GPR55 as Multi-Disease Targets
The G protein-coupled receptor GPR55 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that has been linked to several different diseases or conditions making it a potential therapeutic target. Agonists acting on GPR55 are expected to play a therapeutic role in diabetes, gut mobility, bone turnover, and diseases of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Antagonists are also expected to influence bone turnover, while also affecting treatment of inflammation, pain, cancer, and obesity. Targeting this receptor could therefore provide a means to modulate several different diseases.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsDesign of Short Promoters for Gene Therapy
Gene therapy using space-constrained delivery vehicles like adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors can benefit from the shortening of large tissue-specific promoters. This motivated efforts to make promoters highly compact while maintaining activity and specificity. However, the promoter design process is largely iterative and experimental. It typically involves the synthesis of a promoter fragment roughly up to 3000 nucleotides upstream and ∼50 nucleotides downstream of the transcription start site. Upstream fragments are then truncated until loss of function occurs, indicating the optimal short promoter. However, it may still contain “subsequences” that do not contribute to function. If an alternative solution can be designed to computationally predict the transcription factor binding sites, this would enable removal of non-functional “subsequences” yielding even shorter promoters and in a cost-effective manner.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Research ToolsSpruce Tree Crown Delineation using a Novel Algorithm
Spruce trees dominate boreal and temperate forest biomes and are critical to maintaining the global climate. Accurate counting of individual spruce trees and estimation of their crown span have many applications including forest inventorying, estimating the carbon captured as biomass, assessing tree health, and precision forestry practices. Very-high resolution (VHR) multispectral remote sensing image data of trees are acquired using low-flying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAVs) platforms, whereafter the data are processed to yield the desired tree-level metrics/parameters in a cost-effective manner. Delineation errors occur at crown boundaries of overlapping trees due to a) lack of evident spectral or spatial difference between the neighboring crowns, b) intra-crown spectral variability, c) non-uniform illumination/shadowing, and d) under exploitation of the spectral, spatial contextual, and structural information in VHR multispectral data.
Read more...Keywords:
Novel Compounds for Drug-resistant NSCLC Treatment Identified using a Novel Assay
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadliest cancers worldwide, with an estimated 1.7 million new cases reported annually. Approximately 85% of cases are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), of which 17-78% (depending on geographic region) contain activating mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), with the majority of these mutations corresponding to in-frame deletions in exon19 (ex19del) or a leucine to arginine substitution at amino acid position 858 (L858R). Oncogenic addiction of tumors to these mutant receptors has led to the development and approval of several generations of successful tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapeutics (which specifically target the kinase activity of oncogenic EGFR) for treatment of patients with metastatic NSLCLC. Unfortunately, patients undergoing treatment frequently acquire resistance to these drugs, often through the overexpression of other RTKs or additional mutations in EGFR. For instance, almost 50% of patients treated with the third generation TKI Osimertinib acquire an additional mutation (C797S) that mediates resistance to the drug, and there are currently no approved targeted therapeutic options for patients with this common form of NSCLC. Novel drugs for treatment of patients with mutant EGFR-mediated NSCLC are therefore urgently needed, including both new TKIs and compounds with novel modes of action less susceptible to the development of drug resistance.
Read more...Keywords:
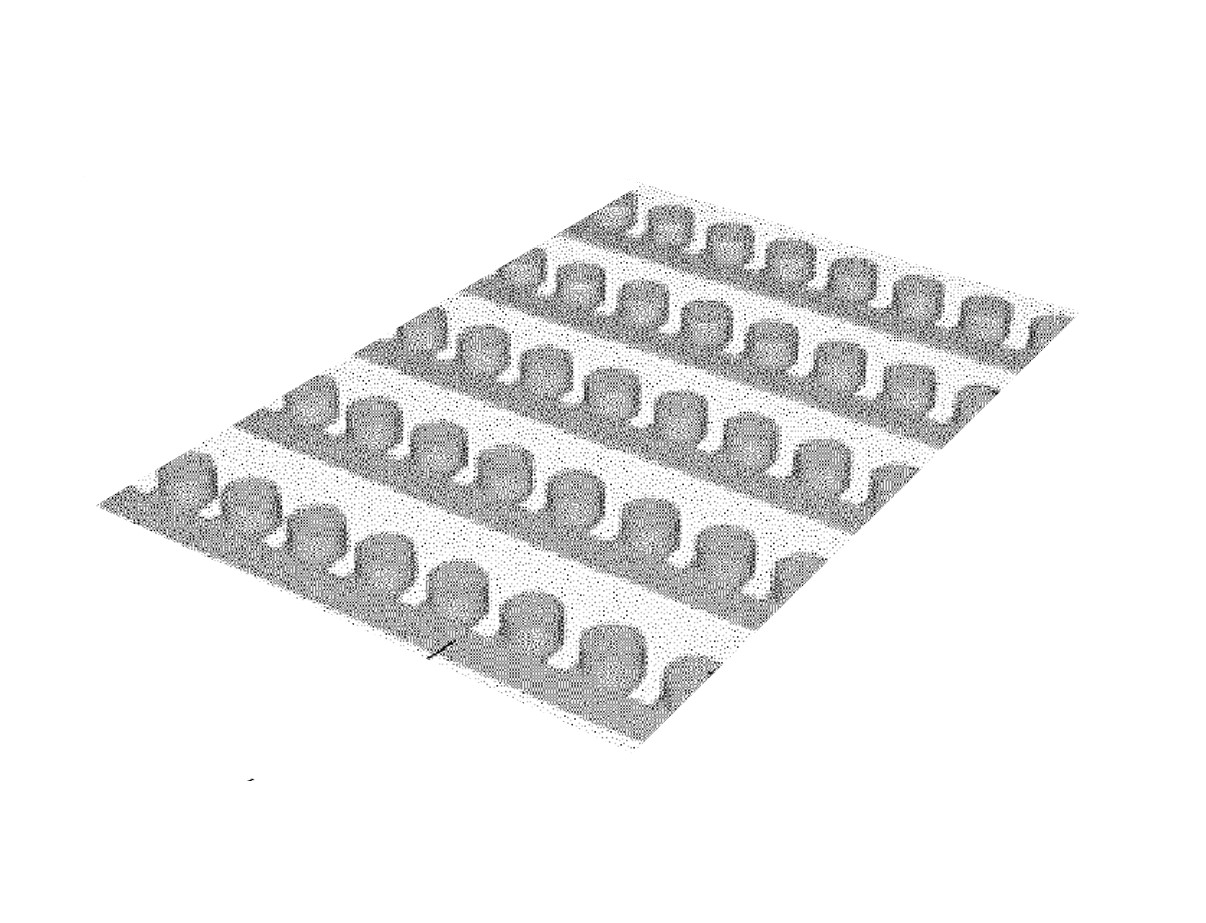
Screening PlatformImprovements to Organ-on-a-Chip Device Architecture
Organ-on-a-chip (OOC) systems recapitulate the complex biological structures and processes that give them the potential to be more predictive of human responses during drug discovery and development. The general design of these devices falls into two categories: laterally adjacent channels in a single plane or vertically stacked single channel arrangements. As such, the structure of these devices restricts the diffusion of nutrients or flow of molecules involved in cell communication to either the lateral or the vertical direction, different from the native 3D diffusional movement found in biological tissues. To be more closely reflective of in vivo conditions, new strategies are necessary to enable multidirectional molecular flow.
Read more...Keywords:
Organ-on-a-chipBiocompatible Microemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poorly Water-Soluble Active Ingredients
Self-Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SMEDDS) is an advanced lipid-based delivery system composed of an isotropic mixture of surfactants and oils that rapidly and spontaneously assemble into microemulsions (5-150 nm) upon exposure to water with a gentle agitation. These features enable enhanced delivery and quick absorption of hydrophobic bioactive compound through gastrointestinal tract and epithelial tissues. SMEDDS are easy to manufacture, offer high loading capacities, and have a long shelf life.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemKidney-On-A-Chip Model with Glomerular Structural Features
Kidney-on-a-chip devices offer the promise to revolutionize the study of disease and the pre-clinical testing of drug compounds, as they possess several advantages over animal models. Since the kidney is a complex organ containing multiple cell types with different roles and functionalities, devices usually recapitulate certain renal structural elements (e.g. tubular structure, collecting duct, proximal tubule, glomerulus) that may be involved in disease. At the glomerulus, podocytes comprise an important part of the filtration barrier and breakdown of their sophisticated branching pattern has been linked to a significant proportion of kidney diseases. Challenges to podocyte organ-on-a-chip (OOC) systems include immature phenotypes and a lack of comprehensive readouts of podocyte function.
Read more...Keywords:
Organ-on-a-chipDetermining Protein-Protein-Interactions for Target Identification and Drug Screening
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) govern many cellular processes and play a crucial role in organism function. There are estimated to be between 130,000-600,000 types of PPIs in the human ‘interactome’. Aberrant interactions have been linked to various diseases like cancer, infectious and neurodegenerative diseases. As such, the identification and modulation of PPIs is an attractive approach to the development of new drugs. There are several techniques available (LuTHy, LUMIER, MAPPIT, KISS, Yeast Two-Hybrid (YTH), PCA, and NAPPA) for the identification of PPIs and these can often be also utilized for drug screening. However, all of them exhibit certain biases that prevent coverage across the human ‘interactome’, thus necessitating the development of complementary techniques.
Read more...Keywords:
Screening PlatformPortable Automated Manufacturing of Protein-Based Therapeutics
Molecular and hardware technologies for automated production and purification of protein-based products.
Read more...Keywords:
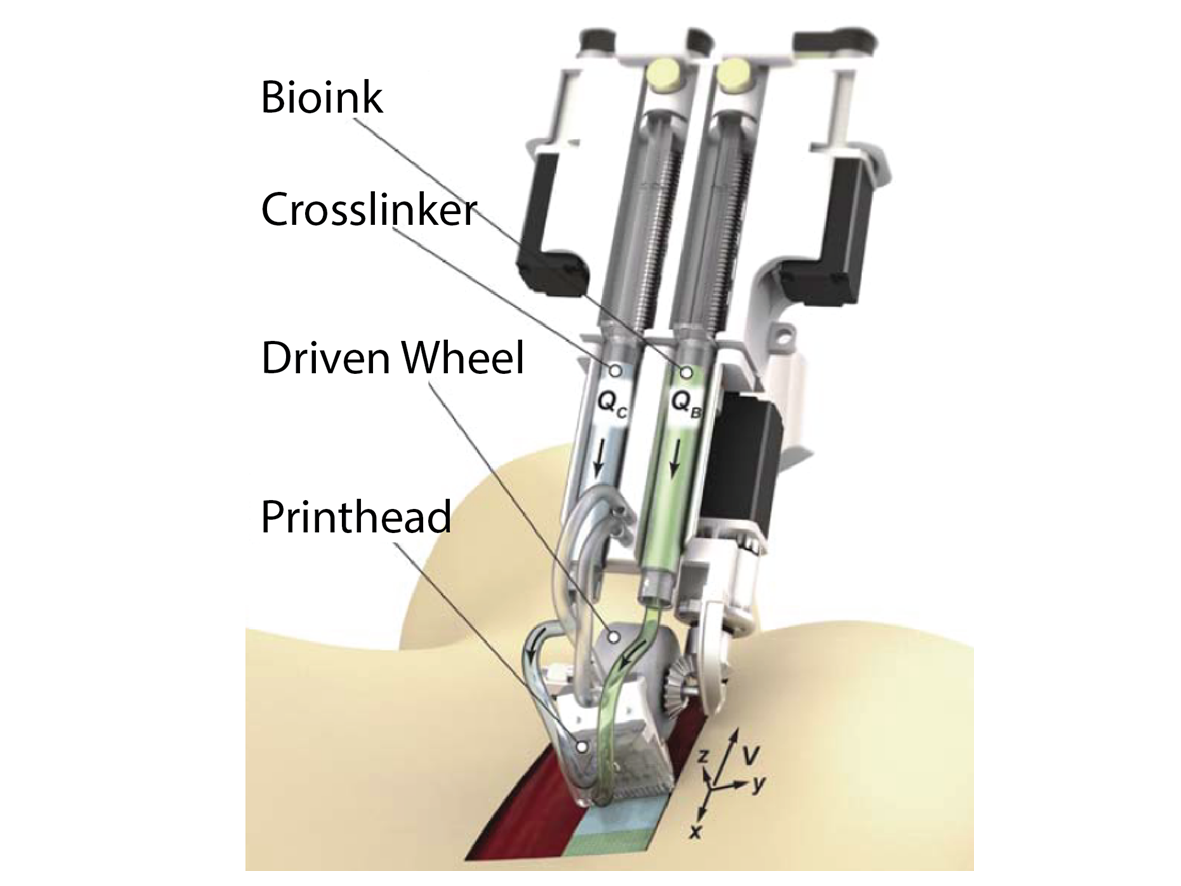
Therapeutics, Sensors & InstrumentationA Handheld Skin Printer for Treatment of Burns and Deep Wounds
Deep skin wounds, such as those caused by burns, are usually treated by harvesting skin from healthy regions of the body and redistributing them onto the wound area. However, challenges arise when large areas are affected and donor sites are scarce. In such cases, the available healthy donor skin is often insufficient for autografting, leaving a large portion of the wounded area either ungrafted, allografted, or uncovered, and resulting in poor outcomes. Use of regenerative cells and materials are one possible solution, with cells often demonstrating a better outcome. However, methods to transfer viable cells onto wound areas remain a challenge.
Read more...Keywords:
Medical Devices, BiomaterialsNovel Nematicides for Animal Health and Plant Applications
Parasitic nematodes are a major problem in agriculture where their infection of livestock and parasitization of plants are a threat to food security and result in billions of dollars of lost productivity. Several classes of nematicides, compounds that are toxic to nematodes, have been approved and successfully integrated into the food generation process. However, two problems with current nematicides are increasing resistance to their effects and serious concerns with their environmental impact, the latter of which has led to withdrawal of commercially successful nematicides from general use. Researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered two small molecule scaffolds for potential use as nematicides in agricultural applications.
Read more...Keywords:
Small MoleculesScalable Sensing Platform for Point-of-Need Testing
Scalable, portable diagnostics for bacteria detection, molecular diagnostics, and immunoassays through microchip-based optical, electrochemical, ion, pH, and temperature measurements.
Read more...Keywords:
Point-of-Care, Chips, Semiconductors, CompaniesHippoCamera: Digital Memory Augmentation
Hippocamera is a memory augmentation technology that aides in the recall and storage of memories. The technology features novel methods to tag and replay recorded moments to promote rich reliving and storage of experiences.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cameras, Communications, Companies, Digital Media, Health & Related Life Sciences, Image & Video Processing, Mobile Apps, Neurological Disorders, Smartphones, SoftwareJALI: Automated 3D Lip Synchronization and Facial Animation
JALI provides products and services for the complete automation of high-end lip sync and facial animation for ultimate animator directorial control.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Animation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Companies, Computer Graphics, SoftwareMulti-Port Converter Structure for DC/DC Power Conversion
The invention is for a new power electronic converter topology suitable for modularly configured solar photovoltaic or battery storage applications
Read more...Keywords:
Automotive, Battery, Energy, SmartphonesSolid-state Optical Atomic Clocks
an optical atomic clock that is both precise enough to detect gravitational waves, and compact and portable enough that it could be put on a satellite. The clock design makes use of a “two-photon transition” in calcium atoms.
Read more...Keywords:
Communications, Computer HardwareMultimodal Spectroscopy Using a Dielectric Grating Coupled to a Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor
This invention is a platform to improve the functionality of the conventional surface plasmon resonance-based sensors.
Read more...Keywords:
Chips, Circuit design, Computer Hardware, Sensors & InstrumentationEmploying Wayfinding and Bottom-Up Knowledge Discovery and Information Flow in Infrastructure and Construction Projects
This invention is a system that presents an original contribution in the form of a knowledge base implemented as an Web Ontology Language (OWL). This system also combines customized wayfinding and recommender systems to support this knowledge base and automate the communication process.
Read more...Keywords:
Construction, Smart CitiesInducing Directed Migration (Translocation) of Neural Cells Using Electric Fields
A clinically-relevant stimulation system can induce directed migration (translocation) of neural precursor cells using asymmetric balanced biphasic electric fields.
Read more...Keywords:
Medical Devices, Neurological Disorders, Sensory Systems & RehabilitationSystem and Methods for Online Socio-Technical Analysis of Buildings
This invention builds around an online system/service that tries to leverage advancements in Building Information Models (BIM), energy-efficiency simulation tools and online social network analysis methods to enable a data-driven approach to building design, planning, construction and maintenance.
Read more...Keywords:
Construction, Smart Cities, SoftwareCrossShade: Automated 3D shading from sketches
CrossShade allows the creation of 3D-looking shaded production drawings from initial concept sketches.
Read more...Keywords:
Computer Graphics, Animation, 3D Imaging, SoftwareCrowdsourced Indoor Localization Using WiFi and Inertial Sensors
The technology uses a combination of sensor information, such as the accelerometer and gyroscope (e.g. from mobile phones or wearable inertial sensors), in addition to WiFi signal strength, to build a system that can achieve accurate location estimation technique for indoor environment.
Read more...Keywords:
Indoor Localization, Sensors & Instrumentation, Smart Cities, SmartphonesiTest: A modular cloud platform for industrial motor testing
iTest is a turn-key and modular software and hardware platform for testing physical motors remotely over the Internet.
Read more...Keywords:
Software, Computer Hardware, Robotics, AutomotiveMonte Carlo Lights: Adaptive Traffic Signal Control
Monte Carlo Lights is a novel ATSC approach that combines state-of-the-art reinforcement learning and Monte Carlo tree search to optimize traffic flow.
Read more...Keywords:
Machine Learning, Automotive, Deep Learning, Software, Smart CitiesRhea: Digital Wellness Platform for Personalized Brain Rehabilitation
Rhea is a rehabilitation platform and startup grounded in science that active recovery to heal and care for the brain.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Companies, Digital Media, Health & Related Life Sciences, Mobile Apps, Neurological Disorders, Sensory Systems & Rehabilitation, Smartphones, Software, Wearable TechPhenoTips: Software for Patient Phenotyping
PhenoTips is a B2B digital health spinout from U of T and SickKids, helping healthcare systems prepare for a future when genetics is a critical part of every patient's routine care. Healthcare workers use PhenoTips through their existing EHRs to manage critical data for genomic medicine,
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Diagnostics, Patient Care, SoftwareODAIA: AI-Driven Customer Journey Intelligence
ODAIA is business intelligence software that enables organizations to understand, predict, and optimize their customer's journeys. The technology leverages AI to facilitate the exploration, analysis, summarization, and optimization of a customer's journey, from awareness to purchase.
Read more...Keywords:
Data Analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Software, Companies, Research ToolsCryosparc: Accelerated Protein Structure Determination from Cryo-EM
High-performance software solutions and advanced algorithms for cryo-EM data processing.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Companies, Drug Discovery, Machine Learning, Research Tools, SoftwareAutoscribe: AI-Powered Voice Assistant for Clinicians
AutoScribe uses hands-free speech recognition and Artificial Intelligence to help reduce time consuming manual clinical documentation, freeing clinicians to place their focus where it should be – on their patients.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Communications, Companies, Deep Learning, Health & Related Life Sciences, Human-Computer Interaction, Machine Learning, Patient Care, Point-of-Care, SoftwareAdaptive Neural Implant for Modulation and Observation (ANIMO)
Invasive and non-invasive hardware and software for vital signs monitoring
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Wearable Tech, Machine Learning, Battery, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Circuit design, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Medical DevicesSelective Enhancement of Electrical Nerve Excitability
Treatment of overactive bladder and other disorders via non-invasive electrical neurostimulation.
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Medical Devices, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Neurological Disorders, Advanced Health Technologies, SoftwareSoftware for simulating stepwise undirected network growth
A method and model for simulating general multi-phase network growth, inspired by the simplified, stepwise behaviours of a unicellular slime mould.
Read more...Keywords:
Smart Cities, Software, ConstructionQuantum-Safe Encryption and Communication
Quantum-proof cybersecurity products and enabling technologies for the Quantum Internet. These technologies offer quantum-safe communication products ready for today's infrastructure, while building key components of the Quantum Internet, including Quantum Repeaters, Quantum Communication Protocols, and Quantum Network Simulators.
Read more...Keywords:
Communications, Companies, Computer Hardware, Cybersecurity, Electrical & Computer EngineeringEEG-Based Image Reconstruction
A method to extract, assess, and visualize information from electroencephalography (EEG) readings.
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Communications, Deep Learning, Health & Related Life Sciences, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, MRI, Neurological Disorders, Research Tools, SoftwareClosed-loop neurostimulator and signal processing methods
Electronic Systems for Monitoring, Diagnosis, and Control of Physiological Disorders
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Chips, Computer Hardware, Diagnostics, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Machine Learning, Medical Devices, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Neurological DisordersCentivizer: An Interactive, Modular Approach to Dementia Care
Centivizer is a modular system that physically, cognitively, and socially stimulates individuals with dementia by providing self-initiated, reward-based activities that can be used 24/7 without needing caregiver support.
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Computer Graphics, Computer Hardware, Digital Media, Health & Related Life Sciences, Image & Video Processing, Mobile Apps, Neurological Disorders, Patient Care, Smartphones, SoftwareBinPro: Tools and Techniques for Binary-Source Code Authentication
BinPro combines static analysis, graph matching and ML to detect and mitigate the threat of maliciously inserted backdoors by conducting binary source code audits.
Read more...Keywords:
Computer Hardware, Cybersecurity, SoftwareColor Sandbox: Smart Swatch Builder
The two inventions captured in this technology allow for the representation, learning, and interactive editing of color palettes through a novel interface for creating color themes.
Read more...