Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies
Serological Assay based on split Tripart Nanoluciferase to detect the activity of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, called neu-SATiN, with potential uses towards COVID-19 disease and vaccine management.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsCancer Treatment Guidance Using F-box or Cyclin Biomarkers
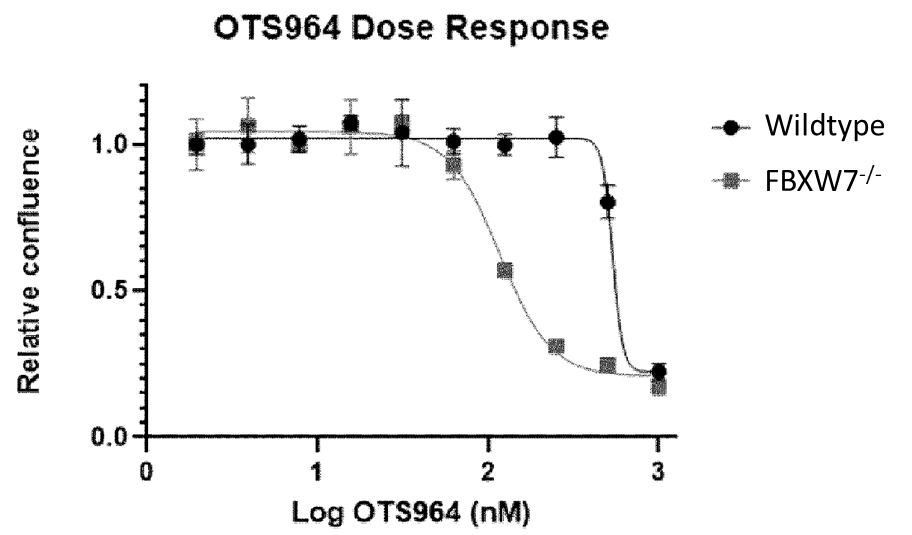
Targeting of the Wnt pathway is an attractive approach to treatment of multiple cancers as it can play a significant role in carcinogenesis. For example, a first-in-class inhibitor (LGK974) of a protein, porcupine, involved in the Wnt pathway has recently completed Phase 1 safety trials. Inhibition of porcupine prevents the palmitoylation of a Wnt signalling protein, an event that otherwise triggers pro-oncogenic outcomes. However, the beneficial impact of this inhibitor in cancer treatment is negated when inactivating mutations to a downstream tumor suppressor protein, FBXW7, are present in a subset of the population. Such alterations in FBXW7 occur at significant frequencies in patients with uterine, colorectal, cervical, and head and neck cancers. Elucidation of the biomolecular consequences of FBXW7 mutations may lead to suggestive mechanisms to treat these subpopulations.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsGenetically Engineered Proteins for Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
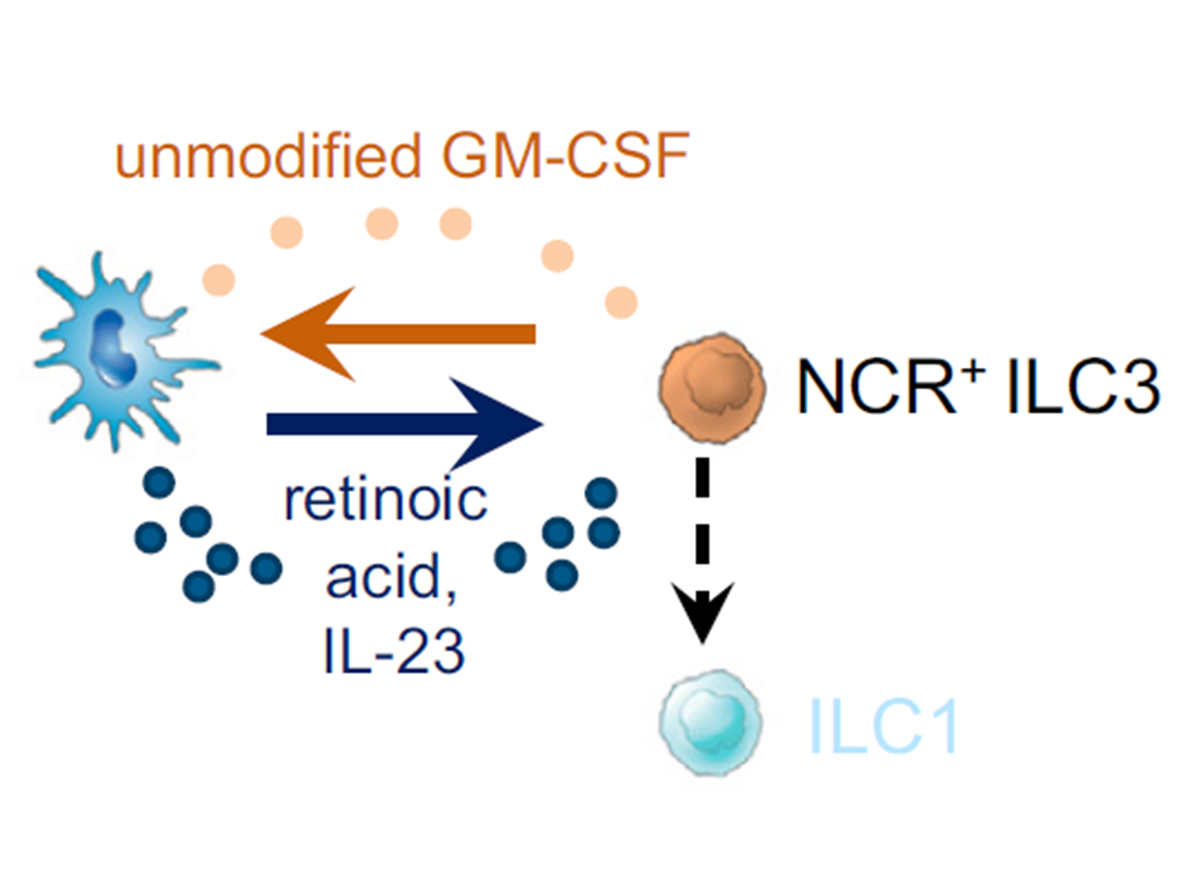
Deregulated balance of the immune system strongly contributes to the development of chronic inflammatory conditions, like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). A critical cellular element in sustaining immune and tissue homeostasis are mononuclear phagocytes (MNP), hematopoietic, migratory cells with superior capability to engulf and kill microbes, as well as priming and sustaining adaptive immune responses. Convincing animal research and accumulating evidence in humans suggest that these cells are fundamental in determining whether the immune system is activated or remains tolerant towards microbes. Key to their regulation, particularly in the intestinal tract, is the cytokine Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF). Every 5th patient diagnosed with Crohn’s disease (CD) displays neutralizing autoantibodies (AuABs) against GM-CSF, posing a possible explanation for why previous phase II clinical trials, despite reporting overall improvement of symptoms, failed to reach statistically significant outcomes. If mechanisms to evade these antibodies can be designed, GM-CSF may prove to be an effective treatment against Crohn’s disease.
Read more...Keywords:
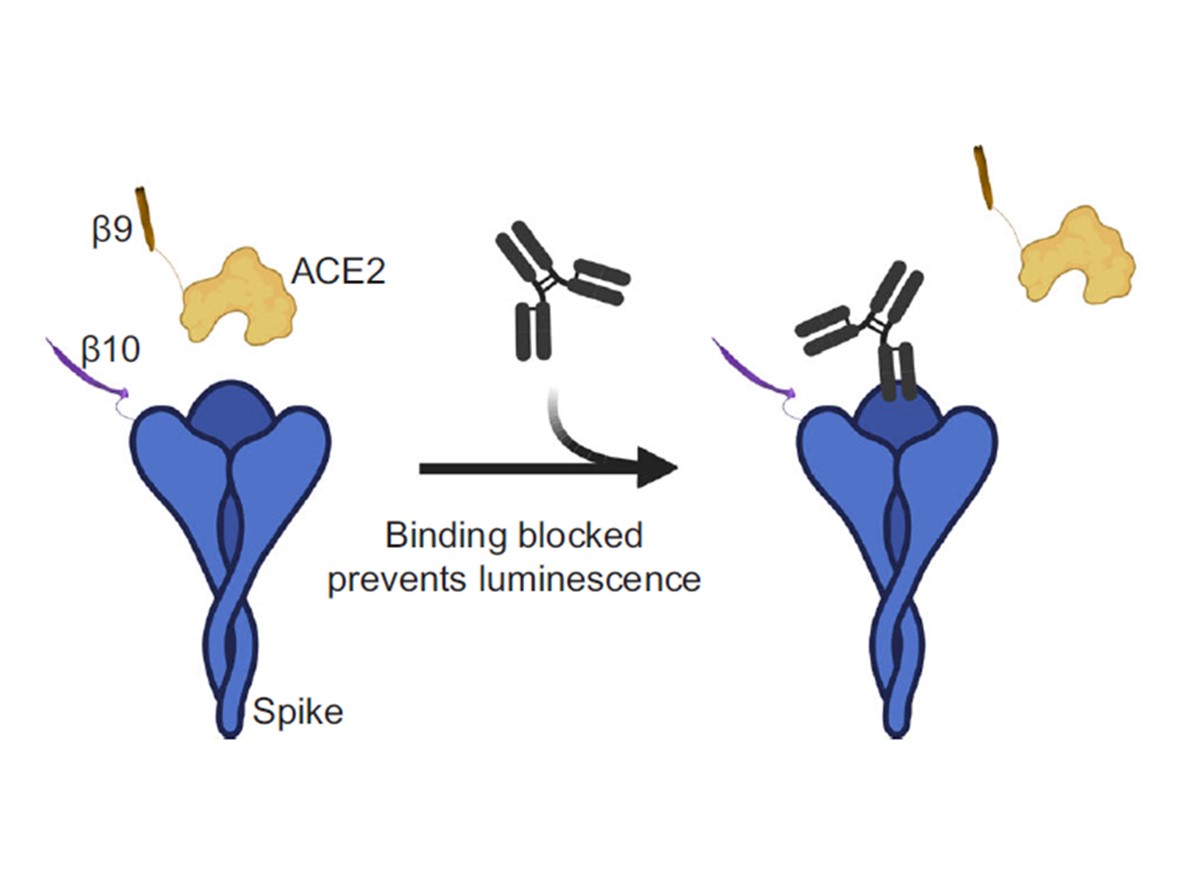
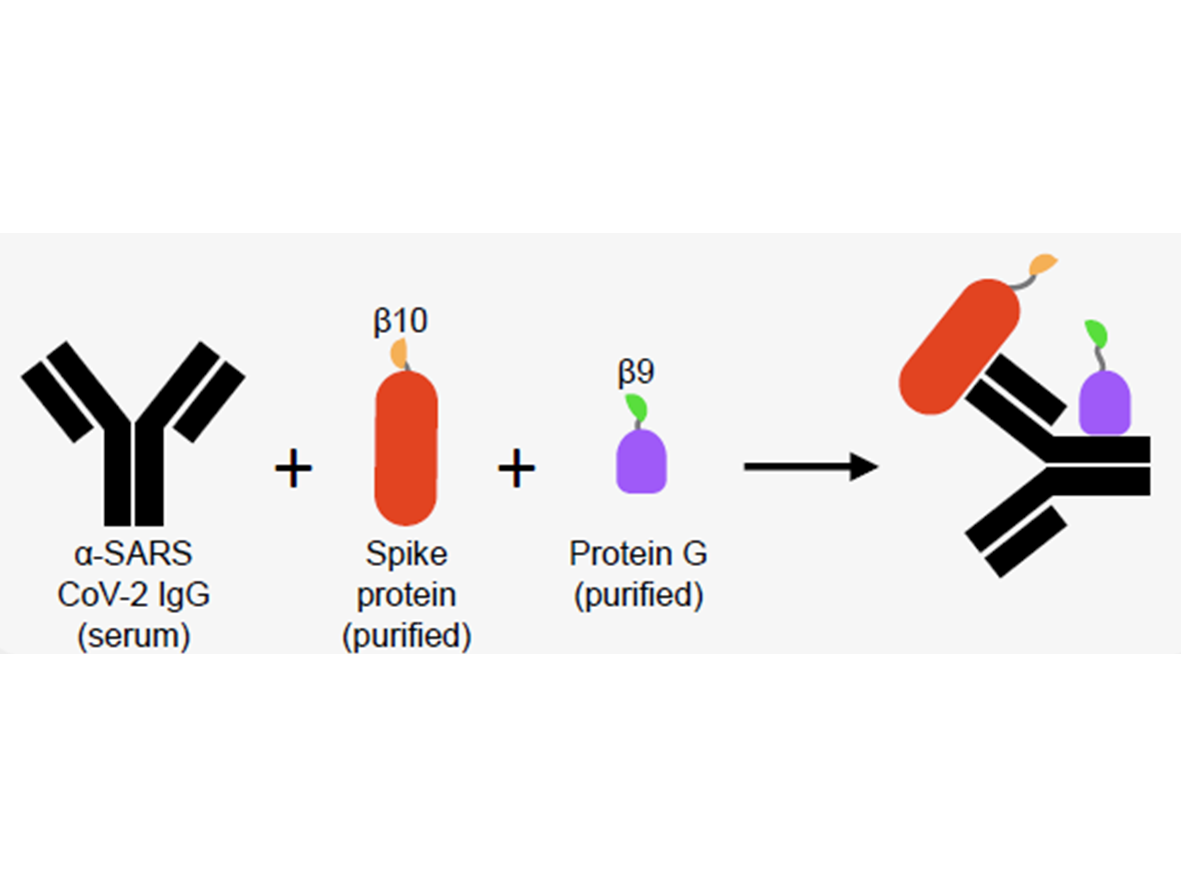
Diagnostics, TherapeuticsAssay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
Serological testing is important for understanding the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus by determining how many people in a given population have been infected. The tests are also used to evaluate the responses to current vaccines against this new coronavirus in people who have already been vaccinated. Though several serological tests have been proposed or are in development, the gold standard is still the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). However, this test is time-consuming (~ 6 hrs), tedious (requires multiple washes), and relatively expensive (~$25/test) offering an opportunity to emerging serological tests of comparable quality for probing immune response.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsNanoparticle-based Thermal Contrast Agents
This invention is a unique concept of developing thermal contrast agents to report the detection of a molecule, cells, or tissues. It utilized nanoparticles as probes in hiological and medical detection. The unique aspect of this research is that it did not utilize the colorimetric or fluorescence properties of a nanoparticle as the detection signal but rather, the heat generated from the nanoparticle. This is very unique concept of developing thermal contrast agents to report the detection of a molecule, cells, or tissues.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsMultiplexed Genetic Detection with Isothermal Signal Amplification
This invention describes a diagnostic platform for viral, bacterial, protozoan, fungal and other infections, which allows an exponential amplification of desired nucleic acid molecules at an isothermal condition and simultaneous detection of multiple infectious genetic biomarkers using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) and Quantum Dot (QD) barcodes respectively. Integrating mobile-cellular devices with multiplex molecular diagnostics can potentially provide the most powerful platform for tracking, managing and preventing the transmission of infectious diseases. With over 6.8 billion subscriptions globally, handheld mobile-cellular devices can be programmed 5 to spatially map, temporally track and transmit information on infections over wide geographical space and boundaries. Here we combined recent advances in quantum dot barcode technology with smartphones to engineer a simple and low-cost chip-based wireless multiplex diagnostic device. This device can analyze 20 μL of sample for multiple genetic biomarkers with an analytical sensitivity of 1 – 5 fmol/μL. The addition of an isothermal amplification step enabled the detection of patients infected with HIV and/or hepatitis B from isolated nucleic acid from serum, and identified viral infection in only 1 hour, after blood collection to final read-out. This device advances the capacity for global surveillance of infectious diseases at or near the point-of-care and has the potential to accelerate knowledge exchange-transfer of emerging or exigent disease threats with healthcare and military organizations in real-time.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsMNAzyme-Based Gold Nanoparticle Sensor
Point-of-care (POC) diagnostics is one of the fastest growing research themes. Simple, cost-effective, and rapid POCs are important to clinicians to make quick and appropriate treatment decisions. This project combines two technologies to create a biosensor that can detect genetic targets, and be further exploited in POC devices. The technology lies on an enzymatic reaction that displays a colorimetric change when specific genetic targets are recognized. This detection strategy is a simple 1- to 2-step assay, low cost, with a better sensitivity than the standard diagnostic technique ELISA. This invention may provide easier and faster POC diagnostics.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsRe-PAIR: A CRISPR-Based Technology for Portable Diagnostics & Biotechnology
Our scientists have engineered a new nucleic acid sensor, based on CRISPR technology, that is cell-free and can be rationally designed for broad applications in portable diagnostics, in sensing and in biotechnology. This novel, portable nucleic acid sensing platform uses a CRISPR technology that, unlike previous technologies, can be deployed outside of the lab without pre-packaged RNA inputs, and can generate multiplexed signals in any reporter mode (e.g. colorimetric, electrochemical, enzymatic, fluorescent). The flexibility afforded by this platform will allow for the sensitivity, resolution and programmability associated with other CRISPR-based diagnostics, but resolves the practical challenges related to their implementation.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsHuman Culture Assay to Assess Muscle Stem Cell Potency
Our researchers have developed an in vitro stem cell mediated skeletal muscle repair platform referred to as “MEndR” (Muscle Endogenous Repair), that accurately recapitulates the timing of key phases of the stem cell (SC) mediated skeletal muscle repair process in a dish (SC-expansion, SC cell cycle exit, SC nascent fiber formation, fiber maturation). Furthermore, this in vitro platform accurately predicts the performance of stem cells at mediating in vivo repair in standard in vivo mouse transplantation assays and has the potential for parallel stratification of the potency of many (100s) drug or cell therapy candidates at enhancing muscle regeneration.
Read more...Keywords:
Diagnostics, Research ToolsIntegrated Quantum Dot Barcode Smartphone Optical Device for Diagnostics
The focus of this technology has been to develop an automated portable device that can extract, amplify, detect, & database the results. This was made possible by the use of innovative engineering approach to assemble each function into a disposable cartridge system. This cartridge system also contains tablets of reagents with known concentrations, so that the device can be portable without the need for refrigeration or unique storage. The detection is then identified by a smartphone camera & databased on a software App.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsIntegrated Quantum Dot Barcode Smartphone Optical Device for Diagnosis of COVID-19
The focus of this technology has been to develop a versatile diagnostic system by using quantum dot barcoding technology in combination with the engineering of a detecting and processing device. This device is proposed to extract, amplify, detect, and database the results, which has been made achievable by the use of innovative engineering approach to assemble each function into a disposable cartridge system. The cartridge system also contains tablets of reagents with known concentrations, so that the device can be portable without the need for refrigeration or unique storage. The detection is then identified by a smartphone camera and databased on an software App.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsRecombinant Antibodies Network (RAN)
The Recombinant Antibody Network (RAN) is a multi-institutional research consortium (member institutions: The University of Toronto, University of California San Francisco and The University of Chicago) created accelerate the identification and development of recombinant antibodies raised against valuable and challenging targets to support drug development and cutting edge biomedical research. The RAN was founded by three ex-Genentech antibody engineers. To date the team has screened and validated over 880 antibodies, some of which are now available for licensing as therapeutics.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Diagnostics, Research ToolsThe Glucose Meter as a Detection System for Point-of-Care Gene Circuit Diagnostics
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on fluorescent reporter proteins which require multi-well plate reader assays, leaving the technology for all practical purposes stuck in the laboratory. In line with this promise of cell free gene-circuit sensors, we have developed a cheap and accessible detection method at the University of Toronto.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsMicro-robotic Capsule for Drug Delivery and Microbiome Sampling
Access to a patient’s GI tract, either for purposes of delivery of therapeutic agents or collecting samples for diagnostic purposes faces a number of challenges. For the former, oral administration, requiring transit through the stomach and upper GI, can impact the stability and solubility of therapeutic agents such as antibodies or probiotics. For the latter, current procedures for retrieving microbiome samples rely on the use of highly invasive endoscopic procedures. Consequently, many diagnoses of gut health (for example to monitor diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or cancer) rely on analysis of a patient’s stool, material that does not reflect the conditions that occur higher up in the GI tract. There is therefore an urgent need for both drug delivery and collection (GI sampling) systems for more effective and precise disease intervention.
Read more...Keywords:
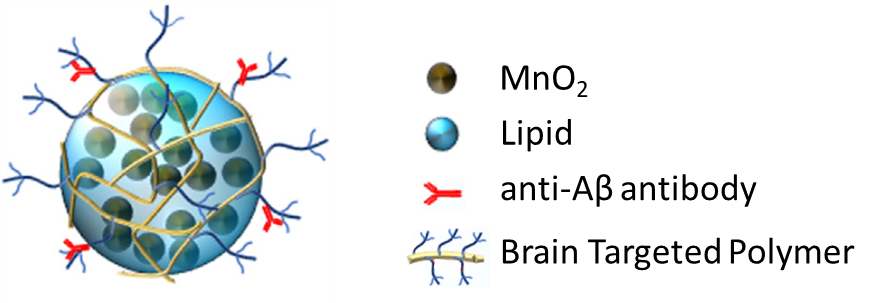
Diagnostics, Research ToolsNanoconstructs for Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia affecting ∼ 5.8 million Americans and 40-50 million people worldwide. Despite the burden of this disease, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s with standard-of-care treatments only able to manage symptoms. Furthermore, clinical diagnosis is imprecise and only suitable for later stages of the disease as it relies on detecting impaired memory and cognitive function, which consequently also results in late intervention. However, changes in neurological biomarkers precede cognitive decline by 15 – 20 years and can thus act as indicators of Alzheimer’s disease enabling early diagnosis and clinical intervention. Though several techniques such as cerebrospinal fluid sampling and various medical imaging methods have demonstrated promise in this regard, none of these have progressed to routine use.
Read more...Keywords:
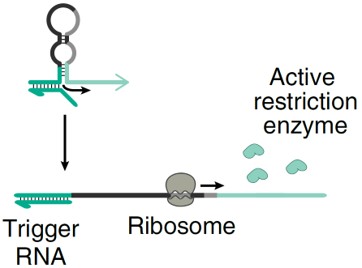
Therapeutics, DiagnosticsPoint-of-Care Detection of Infectious Disease Using Restriction-Enzyme-Based Reporters
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on optical reporter proteins which require equipment contained in centralized labs and which offer limited multiplexing capabilities. To overcome these limitations, researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a direct gene-circuit/electrode interface that allows point-of-care detection of RNA.
Read more...Keywords:
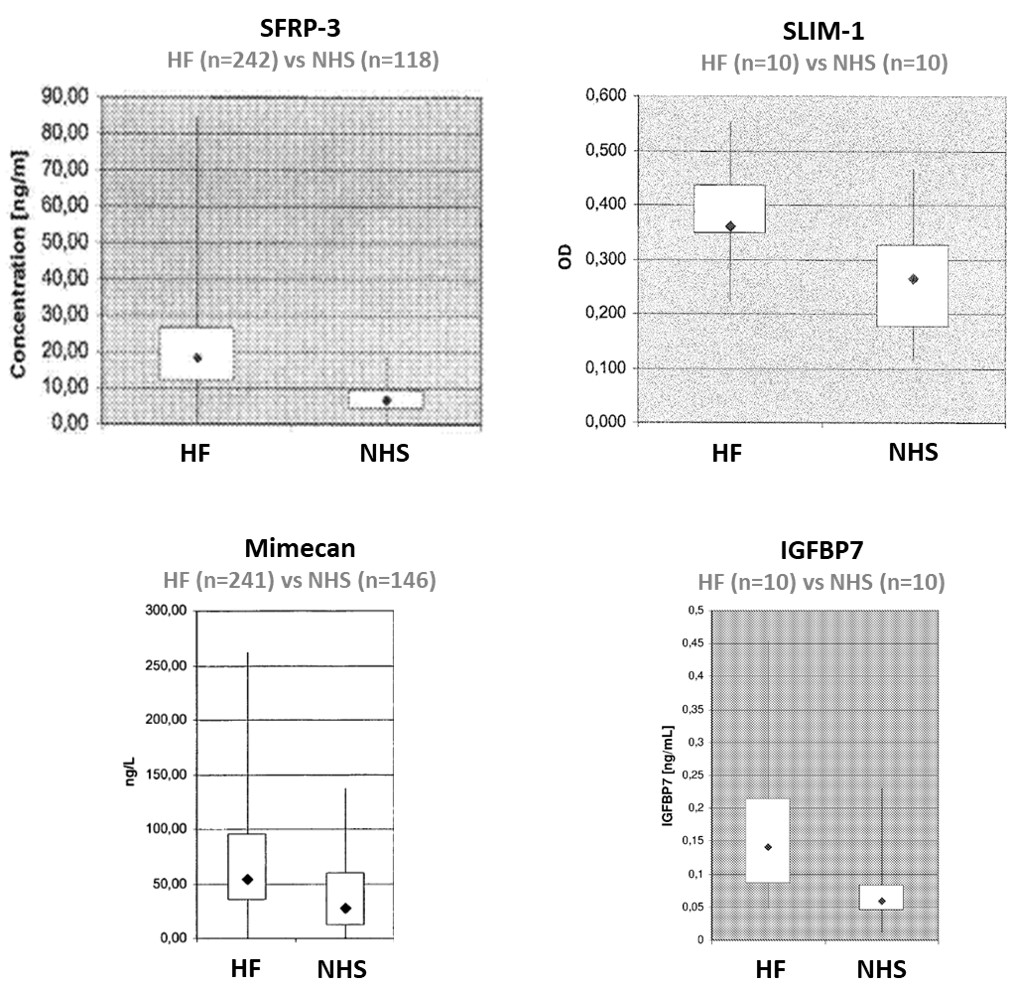
DiagnosticsBiomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF) is one of the most prevalent, costly and life-threatening diseases in developed countries. Early diagnosis of this disease is a challenge as decline in the cardiac output does not occur until the later stages of HF due to certain compensatory mechanisms. Thus, biomarkers are useful in supplementing information from the detection of physical or structural abnormalities by various techniques (e.g. echocardiogram). Natriuretic peptides (particularly NT-proBNP), cardiac troponin, and markers of inflammation are all used in the clinic, though none of them is diagnostic with 100% specificity and 100% sensitivity. New biomarkers, individually or in a panel, can thus improve the current standard of diagnosis or prognosis of HF.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsPhenoTips: Software for Patient Phenotyping
PhenoTips is a B2B digital health spinout from U of T and SickKids, helping healthcare systems prepare for a future when genetics is a critical part of every patient's routine care. Healthcare workers use PhenoTips through their existing EHRs to manage critical data for genomic medicine,
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Diagnostics, Patient Care, SoftwareClosed-loop neurostimulator and signal processing methods
Electronic Systems for Monitoring, Diagnosis, and Control of Physiological Disorders
Read more...