BACKGROUND
Serological testing is important for understanding the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus by determining how many people in a given population have been infected. The tests are also used to evaluate the responses to current vaccines against this new coronavirus in people who have already been vaccinated. Though several serological tests have been proposed or are in development, the gold standard is still the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). However, this test is time-consuming (~ 6 hrs), tedious (requires multiple washes), and relatively expensive (~$25/test) offering an opportunity to emerging serological tests of comparable quality for probing immune response.
INVENTION
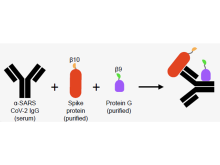
Researchers from the University of Toronto have developed a Serological Assay based on split Tripart Nanoluciferase, called SATiN, to detect IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 with potential uses towards COVID-19 disease and vaccine management. This serological assay gives a readout when three nanoluciferase fragments combine to achieve luminescence (Fig 1). Two of the fragments are attached to components, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and a general IgG-binding protein, that label an anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody. The third fragment then enables detection by binding to the other two fragments and reconstituting the nanoluciferase protein. Using the SATiN assay, proof-of-concept work was conducted on 89 human serum samples (Fig 2) demonstrating its consistency and reproducibility along with a high positive correlation to the gold standard plaque-reduction neutralization test.
Figure: SATiN assay for detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- Test directly performed on human serum (no washes needed)
- Rapid (6x faster), low cost (10x cheaper), and quantitative detection
- Similar sensitivity to ELISA (<5µg/mL); consistent with neutralizing antibody assays
- Very small serum volume needed (~ 5µl)
STATUS
- IP Status
- Provisional patent filed
- Development Status
- Proof-of-concept studies demonstrate the ability to identify the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in 89 human serum samples with similar sensitivity to ELISAs.
Figure 2: Feasibility demonstration of SATiN to detect immune response to COVID-19 in human serum samples from incubation to times points after 20 days. Control serum samples (“Pre-pandemic”) and those from COVID-19 patients show the general increase in luminescence, at different times after symptom onset, indicative of increasing anti-viral antibody generation.