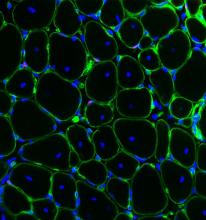
Our researchers have developed an in vitro stem cell mediated skeletal muscle repair platform referred to as “MEndR” (Muscle Endogenous Repair), that accurately recapitulates the timing of key phases of the stem cell (SC) mediated skeletal muscle repair process in a dish (SC-expansion, SC cell cycle exit, SC nascent fiber formation, fiber maturation). Furthermore, this in vitro platform accurately predicts the performance of stem cells at mediating in vivo repair in standard in vivo mouse transplantation assays and has the potential for parallel stratification of the potency of many (100s) drug or cell therapy candidates at enhancing muscle regeneration.
OPPORTUNITY
Targeting and boosting the function of tissue resident stem cell populations is an emerging strategy to heal tissue injuries and cure disease. For example, in conditions such as aging, or muscular dystrophy, muscle stem cells (MuSCs) are present in the tissue but are reduced in regenerative potency. Drugs to stimulate MuSC activity and the localized transplantation of MuSCs are each considered promising strategies to restore skeletal muscle strength and endogenous repair function. A bottleneck to translating discovery-based research in this area to the clinic, however, is the reliance on in vivo functional assays in mice to validate lead candidate molecules. These functional assays are slow, expensive, and require specialized training. To close this gap, researchers at the University of Toronto have developed an in vitro cell potency assay using human cells that enables an assessment of MuSC potency and predicts in vivo transplantation outcomes arising from a gold-standard mouse assay.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
The platform provides, to their knowledge, the only in vitro assay to assess the functional capacity of skeletal stem cells to mediate skeletal muscle fibre repair. The power of this technology is therefore that it potentially provides the ability to:
- Identify and test new compounds that can modulate endogenous stem cell activity or stem cell transplantation outcomes in the context of muscular dystrophies or due to disease, injury or aging;
- Provide a cellular mechanism of action;
- Assess the quality of human muscle stem cell batches manufactured for cell therapy applications (a high-volume quality control application);
- Combine the screening and validation of molecules to modulate muscle stem-cell mediated repair into one step, saving time, money and enabling companies to validate a significantly greater number of hits.