BACKGROUND
Genome wide knockout screens can be used to elucidate genetic pathways and identify novel drug targets. They work by analyzing the impact of gene inactivation on a measured physiological readout, such as cell survival. CRISPR-Cas9 is a simple and effective tool used to disrupt single genes on a large scale. However, generating the necessary pooled libraries to simultaneously inactivate two or more genes (i.e. double knockout) is challenging. Furthermore, other limitations that impact its efficiency exist, such as recombination between duplicated promoters and expression cassettes. Cas12a has been proposed as an attractive alternative to Cas9 as its intrinsic RNAase activity can be used to generate multiple distinct gRNAs from a single concatemer. However, it too has its deficiencies, such as a low double knockout efficiency (<15%). Thus, there is a need for improved techniques to probe genetic interactions (GIs) between two or more gene participants.
TECHNOLOGY
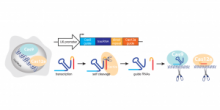
Inventors at the University of Toronto have engineered a new hybrid CRISPR system (Cas Hybrid for Multiplexed Editing and screening Applications or CHyMErA) that is based on the dual expression of the two orthogonal Cas nucleases Cas9 and Cas12a and the delivery of hybrid guide RNA (hgRNA) libraries (Figure 1). The hybrid system combines the DNA editing activity of Cas9 and Cas12a together with the RNA processing activity of Cas12a, which allows mature Cas9 and Cas12a guide RNAs to be generated from a single hgRNA template (Figure 1). With this technique, pooled libraries can be easily generated for higher-efficiency knockouts of a single gene or of multiple genes, with the latter enabling better screening of interactions between two or more genes.
Figure 1. Overview of CHyMErA. A hgRNA consisting of a fusion of Cas9 and Cas12a gRNAs is expressed under a single U6 promoter. Cas12a RNA processing activity cleaves hgRNA to generate functional Cas9 and Cas12a gRNAs. The separated gRNAs can each pair with their corresponding proteins (Cas9/Cas12a) to target two separated genes for knockout. This technique can be used to generate pooled libraries for genome-wide screening of genetic interactions.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- Outperforms genetic screens using Cas9 or Cas12a (Figure 2)
- Cas12a gRNA optimization
- Machine learning-optimized libraries of hybrid Cas9-Cas12a guide RNAs for enhanced binding efficiency
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY STATUS
- PCT filed (Jun 2020; WO2020240523A1)
PROJECT STATUS
The CHyMErA system has been developed and comparatively tested to Cas9 and Cas12a systems for exon deletion efficiency (Figure 2). Deep learning was used to optimize Cas12a gRNAs for more efficient performance. Two pooled libraries have been generated: a paralog and dual-targeting library, and an exon-deletion library (Addgene).
Figure 2. High efficiency exon deletion using CHyMErA over Cas9 and Cas12a. PCR assay monitoring of exon deletion efficiency using paired Cas9 intronic guides (left), paired Cas12a intronic guides (middle) or CHyMErA (right). Efficiency of exon deletion is given below each lane.