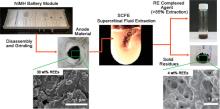
A novel “aerio-metallurgical” process to recycle critical rare earth elements, namely neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), and dysprosium (Dy), from postconsumer NdFeB magnets utilized in wind turbines.
The new process utilizes supercritical CO2 as the solvent, which is safe, inert, and abundant, along with tributylphosphate-nitric acid (TBP-HNO3) chelating agent and 2 wt% methanol as co-solvent.
Achieved 94% Nd, 91% Pr and 98% Dy extraction with only 62% iron co-extraction and minimal 2 waste generation.
Karen Temple
Innovations & Entrepreneurship Manager
Innovations & Partnerships Office (IPO)
(416) 978-3548