BACKGROUND
The Hippo signaling pathway is a key regulator of cell proliferation and cell death. High cell density and stress activate the pathway to stop cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. It has consequently been linked to diseases such as cancer and fibrosis. At the molecular level, the Hippo kinase cassette controls the activity of the transcriptional regulators, YAP and TAZ, through phosphorylation events (Figure 1a). Phosphorylation of YAP and TAZ by a kinase of the Hippo pathway, LATS, results in cytoplasmic localization where these molecules cannot exert their function. However, unphosphorylated YAP and TAZ localize to the nucleus where they can interact with transcription factors (e.g. TEAD) to turn on gene transcription and promote pro-fibrotic and pro-oncogenic outcomes and contribute to resistance to chemotherapeutics. This implies that molecules that promote YAP and TAZ phosphorylation can act as therapeutics for fibrosis and cancer and could overcome chemotherapeutic resistance.
TECHNOLOGY
Researchers at the University of Toronto have identified a kinase, NUAK2 (& the closely related NUAK1), that promotes YAP and TAZ oncogenic and fibrotic activity. NUAK2 acts in a positive feed forward loop where it prevents the phosphorylation of YAP and TAZ by a Hippo kinase (Figure 1b). They have shown that gene knockdown or small molecule inhibition of NUAKs restores pathway activity and inhibits both tumorigenic and fibrotic properties in cells and in mice models. In collaboration with the OICR Drug Discovery Program, the group has undertaken efforts to identify novel potent small molecule inhibitors of NUAKs. Numerous experimental tools, including in-vitro and cell-based assays (in low & high-throughput formats) have been developed to measure Hippo pathway activity confirming on-target effects. Through these efforts, the team has generated novel inhibitors (currently in the advanced lead optimization stage) of the NUAKs that demonstrate potent activity in both cell-based assays and animal studies.
Figure 1. Hippo signalling pathway. a. Extracellular cues turn on the Hippo pathway which results in phosphorylation and cytoplasmic retention of YAP/TAZ; unphosphorylated TAP/TAZ localise to the nucleus where the exert pro-oncogenic, pro-fibrotic functions. b. Negative regulation of the Hippo pathway by NUAK2 promotes oncogenesis and fibrosis.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- NUAK1 and NUAK2 are elevated in broad disease indications based on Cancer and Fibrosis
- Two classes of novel inhibitor compounds for NUAKs: IC50 in the low nM range
- Advanced lead optimization stage
- > 1000 molecules synthesized
- Favourable drug-like properties
- Kinome screening performed (Eurofins)
- Desirable PK/ADME properties (e.g. orally bioavailable)
- Clinical biomarkers known
- Drug screening capabilities: Identification of NUAK2 as a negative regulator of Hippo provides a new opportunity to develop kinase inhibitors that would counteract the oncogenic functions of YAP/TAZ.
APPLICATIONS
- Cancer therapeutic - either alone or in combination
- Multiple solid cancers: breast, colon, ovarian, HNSCC, bladder, others
- Fibrosis therapeutic
- Kidney, lung, liver, pancreas, others
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY STATUS
- National Phase Entry (Jan 2022) for two classes of compounds: AU, CA, CN, EU, JP, US
PROJECT STATUS
Proof-of-principal studies have been conducted in cell lines and mouse models of cancer and fibrosis. Two classes of NUAK inhibitors have been developed.
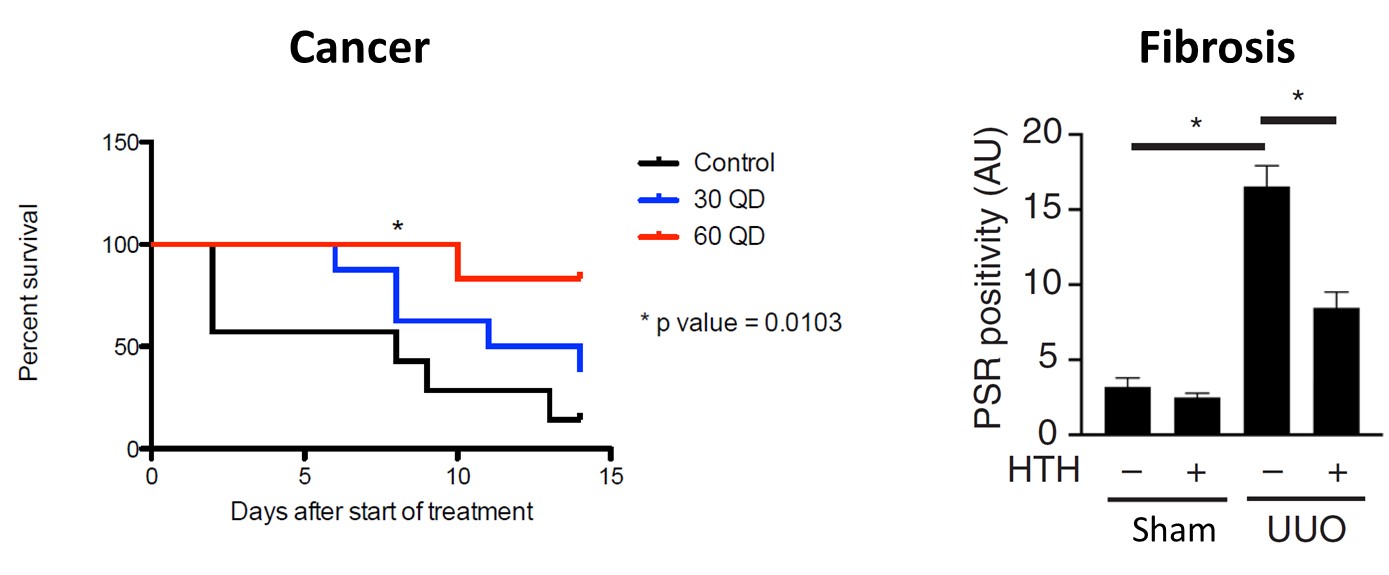
Figure 2. A small molecule compound (NUAK inhibitor) inhibits tumor growth in a late-stage breast cancer model (orthotopic MDA-MB-231) in immunocompromised (NSG) mice leading to increased survival. A known NUAK inhibitor (HTH) decreases fibrillar collagen (measured by Picrosirius red (PSR)) in a UUO-induced renal fibrosis mouse model. Similar decreases in type 1 collagen and α-smooth muscle actin were also found upon treatment with HTH.