BACKGROUND
CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1) is a class 2, type V endonuclease that has revolutionized diagnostics and biotechnology due to its programmable specificity. It performs cis-cleavage of dsDNA (or ssDNA) targets and indiscriminate trans cleavage of ssDNA. Traditional Cas12a-based diagnostics require a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) for target recognition, which limits their application. Additionally, the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and RNA targets remains challenging. Consequently, elimination of dependence on a PAM in the target sequence and improved detection of RNA targets can help realize the full potential of Cas12a for nucleic acid detection.
TECHNOLOGY
Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed RAPID (RNA/DNA Advanced chimeric, PAM-free, Integrated Nicking, Diagnostics), a novel PAM-independent nucleic acid detection platform that expands the capabilities of Cas12a to include RNA and DNA targets without PAM constraints. RAPID leverages the introduction of nicks within the protospacer region to modulate Cas12a trans cleavage activity (Figure 1). By strategically placing nicks, RAPID can detect target RNAs and DNAs (Figure 2), which can be ligated in situ to create hybrid protospacer-targets with trans cleavage activity matching conventional Cas12a. The platform uses RNA and chimeric (mixed RNA/DNA) reporter sequences to reduce non-specific cleavage and improve the signal-to-noise ratio. RAPID is compatible with isothermal amplification methods such as EXPAR and RT-LAMP, enhancing its sensitivity and specificity for clinical diagnostics.
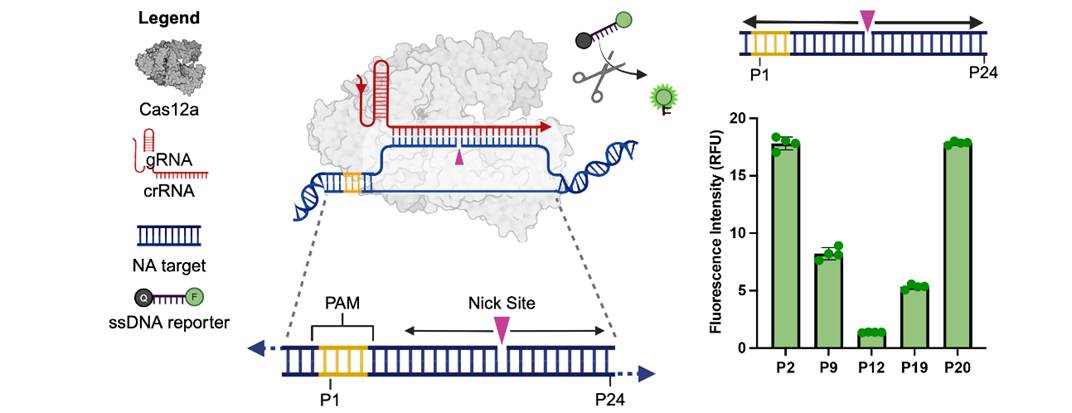
Figure 1. Demonstration of tunable activation of the RAPID system, based on the nick location within the dsDNA. Complete activation is observed at positions P2 and P20, partial activation at P9 and P19, and no activation at P12.
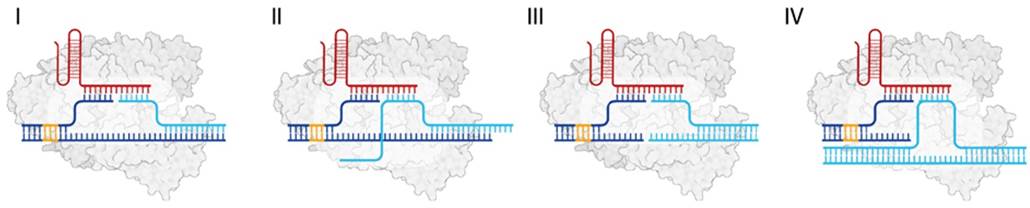
Figure 2. PAM-free detection of various nucleic acids using RAPID; configurations show short (I) and long single-stranded (II) nucleic acids, and short (blunt-ended) (III) and long double-stranded (IV) DNA (dsDNA). Dark blue represents the PAM duplex, red the gRNA, cyan the target strand, and orange the trans PAM.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- PAM-Free Detection: Eliminates the requirement for a PAM sequence, expanding the range of detectable targets.
- High Sensitivity: Achieves attomolar sensitivity, comparable to RT-qPCR.
- Versatility: Detects a wide range of nucleic acids, including miRNA, RNA, ssDNA, and dsDNA.
- Enhanced Specificity: Improved detection of single point mutations (e.g. viral variants)
- Reduced Background Noise: Utilizes chimeric reporters to minimize non-specific cleavage.
- Fast: 5 - 30 min (100 copies/µL vs 0.1 copies/µL)
APPLICATIONS
- Molecular Diagnostics: Detection of viral and bacterial pathogens with high sensitivity and specificity.
- Genetic Testing: Identification of SNPs and genetic mutations for personalized medicine.
- Cancer Research: Detection of miRNA biomarkers for cancer prognosis and diagnosis.
- Environmental Monitoring: Detection of pathogens or contaminants in environmental samples.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY STATUS
- PCT application (February 2025)
PROJECT STATUS
RAPID has been successfully developed and validated with clinical samples, demonstrating 100% concordance with RT-qPCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection in samples with Ct values ≤33.
KEYWORDS
PAM-Free Detection, CRISPR-Cas12a, Molecular Diagnostics, RNA Detection, DNA Detection, SNP Detection, Isothermal Amplification, RT-LAMP, Chimeric Reporters, High Sensitivity, Genetic Testing, Cancer Biomarkers, Environmental Monitoring, Virus, Bacteria