BACKGROUND
Nanoparticle-based assays have revolutionized diagnostic testing by enabling sensitive and specific detection of biological and chemical targets. Among these, quantum dots (QDs)—semiconductor nanocrystals with unique optical properties—have emerged as powerful tools due to their high brightness, tunable emission spectra, and resistance to photobleaching. These features make quantum dots particularly attractive for multiplexed assays and long-term imaging applications. However, the sensitivity of such assays can still be limiting, especially when detecting low-abundance analytes. There is a pressing need for amplification strategies that are compatible with quantum dots to improve detection limits and broaden the utility of QD-based diagnostics.
TECHNOLOGY
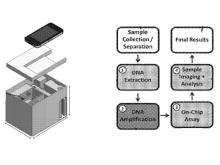
Researchers at the University of Toronto have used isothermal amplification to improve the sensitivity of their QD barcode microbead-based sandwich assay (see P1682). This multiplexed assay can detect target material at femtomole levels, which is still about 100-fold higher than that needed to detect many infections that have low-abundance target analytes. Consequently, they introduced an isothermal amplification step that reduces the limit of detection to clinically relevant levels. They have further packaged this process into a microfluidic device to automate the assay steps which include: extraction of DNA from collected patient samples, nucleic acid amplification, conduction of the QD barcode assay on a chip, and processing and analysis of a collected image (Figure 1).
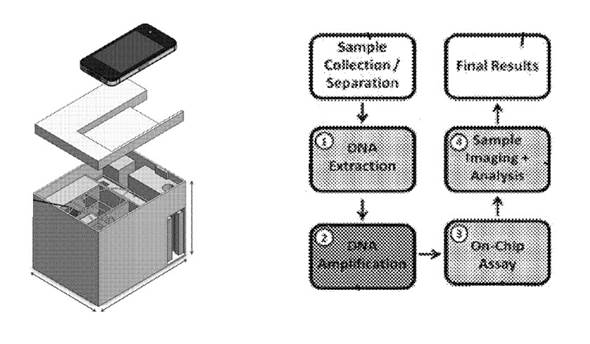
Figure 1. A representation of a device (left) which includes capabilities to conduct steps (right) in a method for detecting pathogen targets from patient sample to imaging and analysis.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- Enhanced Sensitivity: Amplifies signal strength by using isothermal amplification
- ~100 fold lower LoD than lateral flow immunoassays
- Femtomole detection without isothermal amplification
- Attomole detection with isothermal amplification
- Improved Detection of Low-Abundance Targets: Particularly useful in early-stage disease diagnostics or trace contaminant detection.
- Scalable and Cost-Effective: Uses commercially available reagents and standard lab equipment.
APPLICATIONS
- Clinical diagnostics (e.g., infectious diseases, cancer biomarkers)
- Environmental monitoring
- Food safety testing
- Research assays requiring high sensitivity
- Point-of-care diagnostic platforms
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY STATUS
- Granted US Patent (US11248255B2)
PROJECT STATUS
Multiplexed detection of genetic biomarkers from the bloodborne viruses (human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV)) has been demonstrated.
KEYWORDS
nanoparticle assay, signal amplification, biosensing, diagnostics, gold nanoparticles, multiplex detection, low-abundance analyte, point-of-care, pathogen detection