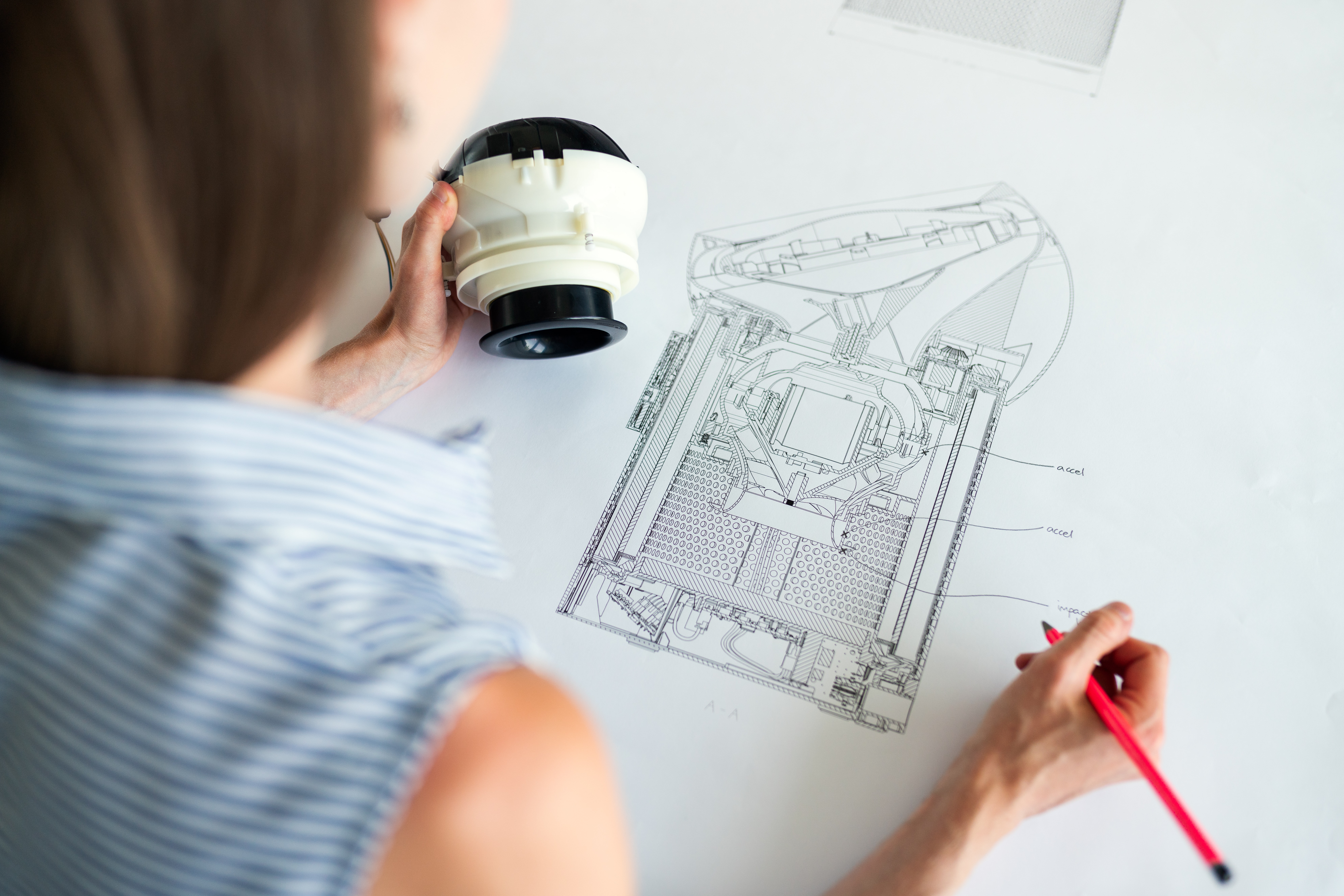
Dynamic, Pixelwise Image Sensing and Systems
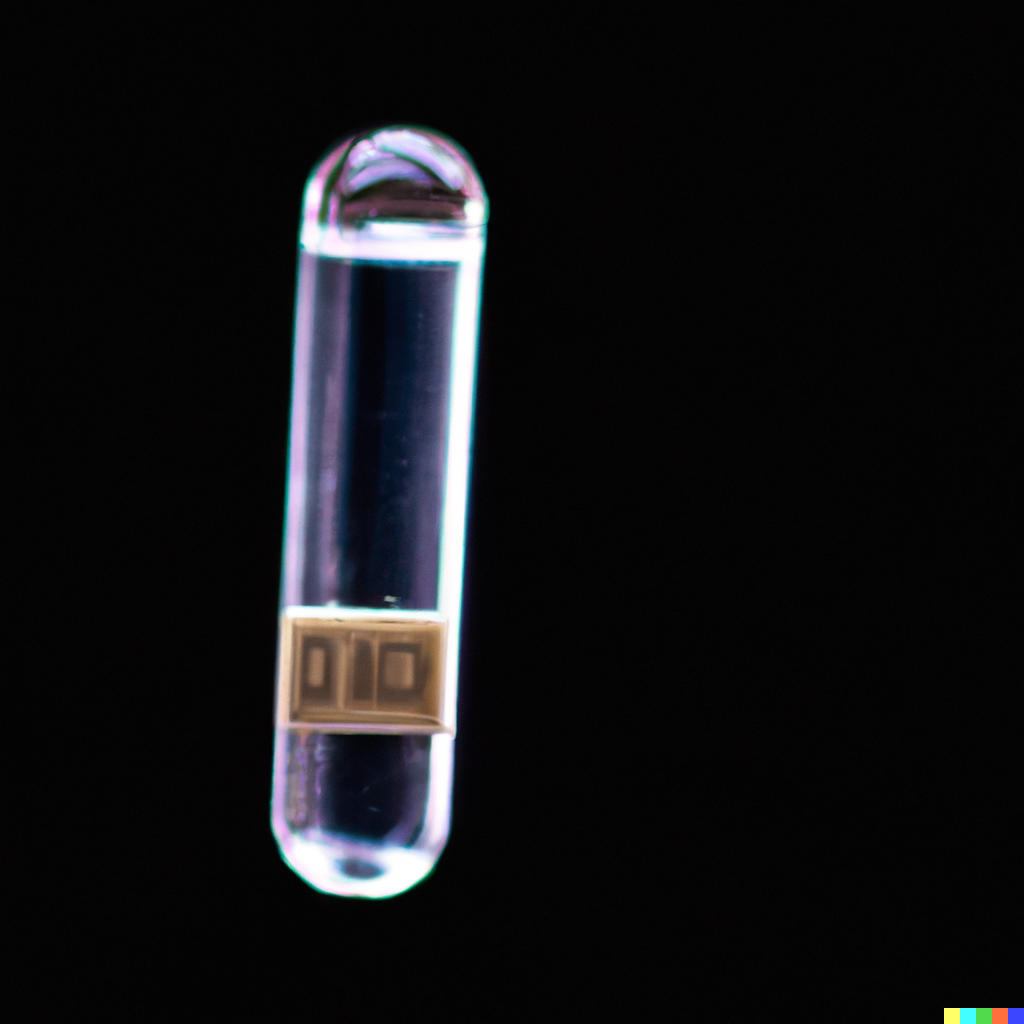
This technology includes a suite of inventions, including a fully-functional coded-exposure-pixel (CEP) camera prototype, a novel programmable CMOS sensor, and a method for adaptive adjustment of exposure of every pixel, based on changes in the brightness of the scene for that pixel to extend dynamic range at native sensor resolution.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Cameras, Circuit design, Computer Graphics, Computer Hardware, Software, Image & Video Processing, SemiconductorsPrevention of Dental Diseases using Novel Bacterial Peptides
Dental diseases are often caused by a perturbation in the balance of the oral microbiome. Bacterial species that confer positive health benefits may reduce in number shifting the oral composition to more virulent strains and increasing the chance of disease. This harmful shift can be reversed by using commensal bacteria to target and crowd out these pathogens. Researchers at the University of Toronto have isolated a Streptococcus salivarius strain (SALI-10) that can interfere with the growth of periodontal pathogens.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsAI-Powered Remote Patient Monitoring Platform
The platform allows for clinical-grade data analysis from wearable sensors (e.g. smartwatches, mobile devices) through proprietary machine learning (ML)-based algorithms that extract clinically relevant data and filter out unreliable sensor data. This platform can provide real-time feedback on patient health, generate more accurate predictions, and enable actionable insights and recommendations to improve care.
Read more...Keywords:
Remote Monitoring, Advanced Health Technologies, Wearable Tech, Health & Related Life Sciences, Software, CompaniesAppetite-Suppressing Cytokinin for Weight Loss and Obesity Treatment
Obesity has increased to pandemic levels and is associated with an increased risk of metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease and cancer. While the most effective means to reduce weight is healthy eating and exercise, adherence to these recommendations are a challenge, especially in individuals with a high body weight or BMI >30. Alternatives to these solutions include anti-obesity therapeutics and supplements. Limited therapeutic options are approved by the FDA, such as Glp-1R agonists, but they are restricted to high BMI patients, are costly for insurers/individuals, have limited efficacy or have unpleasant side effects. Similarly, several supplements are available, but none are regarded as being efficacious unless combined with diet and exercise. Consequently, an unmet need in effective weight loss management exists especially for those individuals in the BMI range of 25 – 32 who want to lose a few pounds to avoid the progression towards metabolic disease without altering their current lifestyle.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsSelective Bioactivatable Nematicides for Crops
Plant parasitic nematodes are microscopic worms that impose a severe economic burden on the agricultural industry. To curtail their effects, chemical agents that reduce the fitness of nematodes, called nematicides, have become widespread throughout the world. However, the ecological toxicity and human safety of these chemicals has posed a problem and resulted in bans to some of the most used nematicides. Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed the first bioactivatable nematicides.
Read more...Keywords:
Small MoleculesSelective HDAC6 Inhibitors for Neurodegenerative Disease
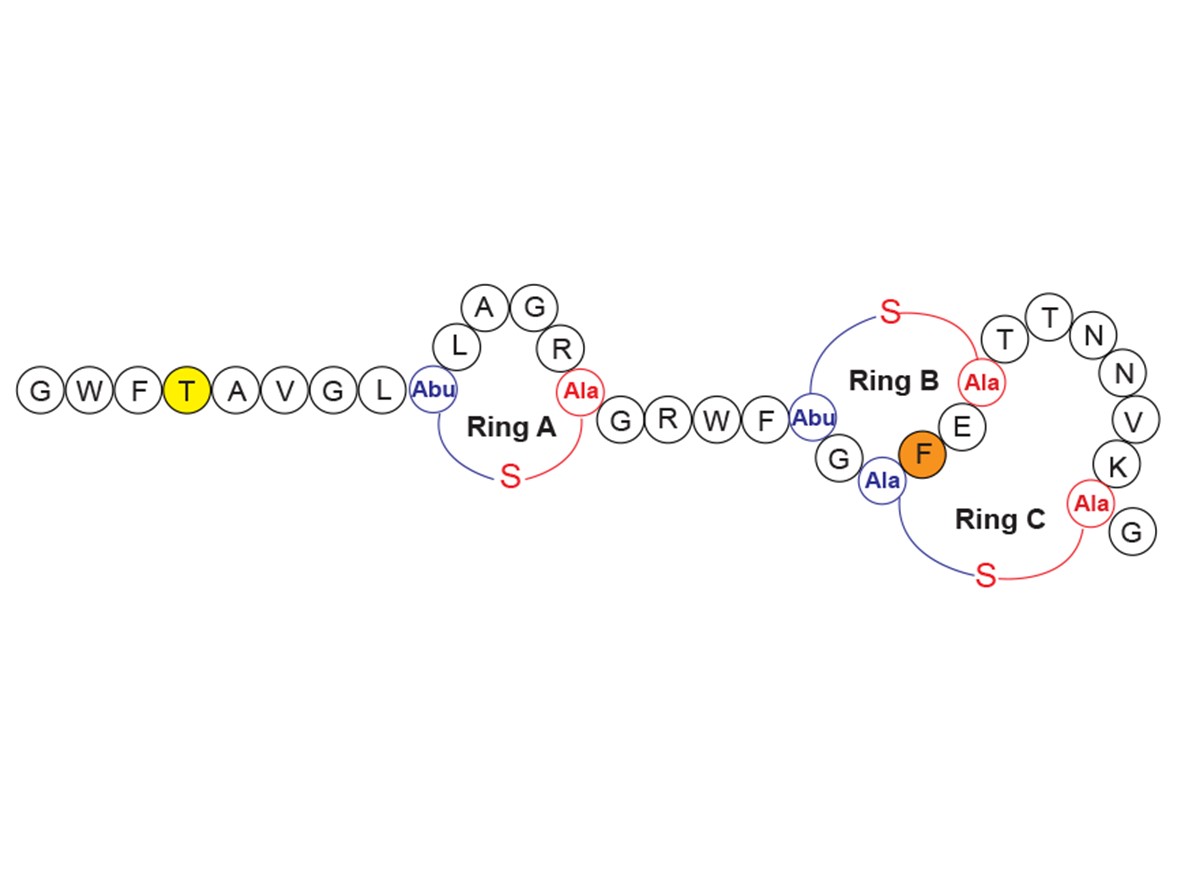
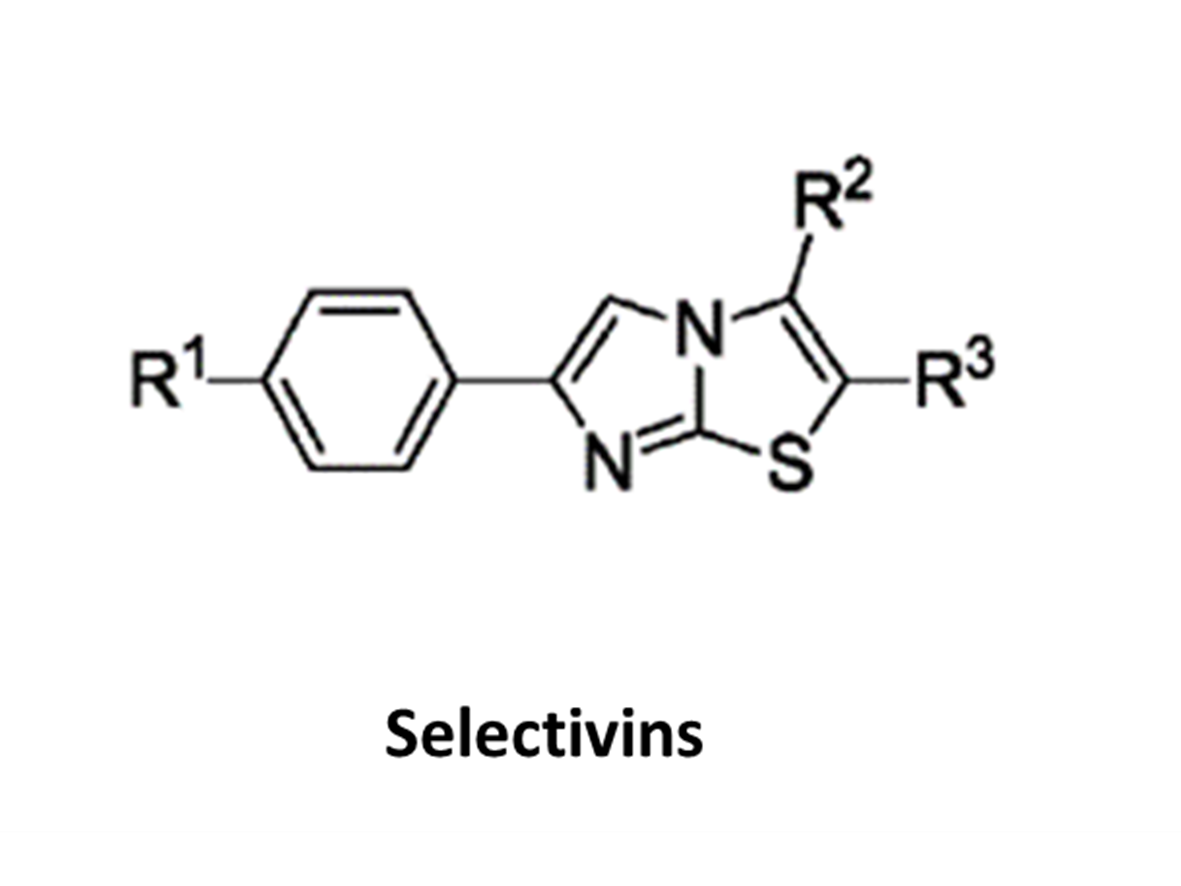
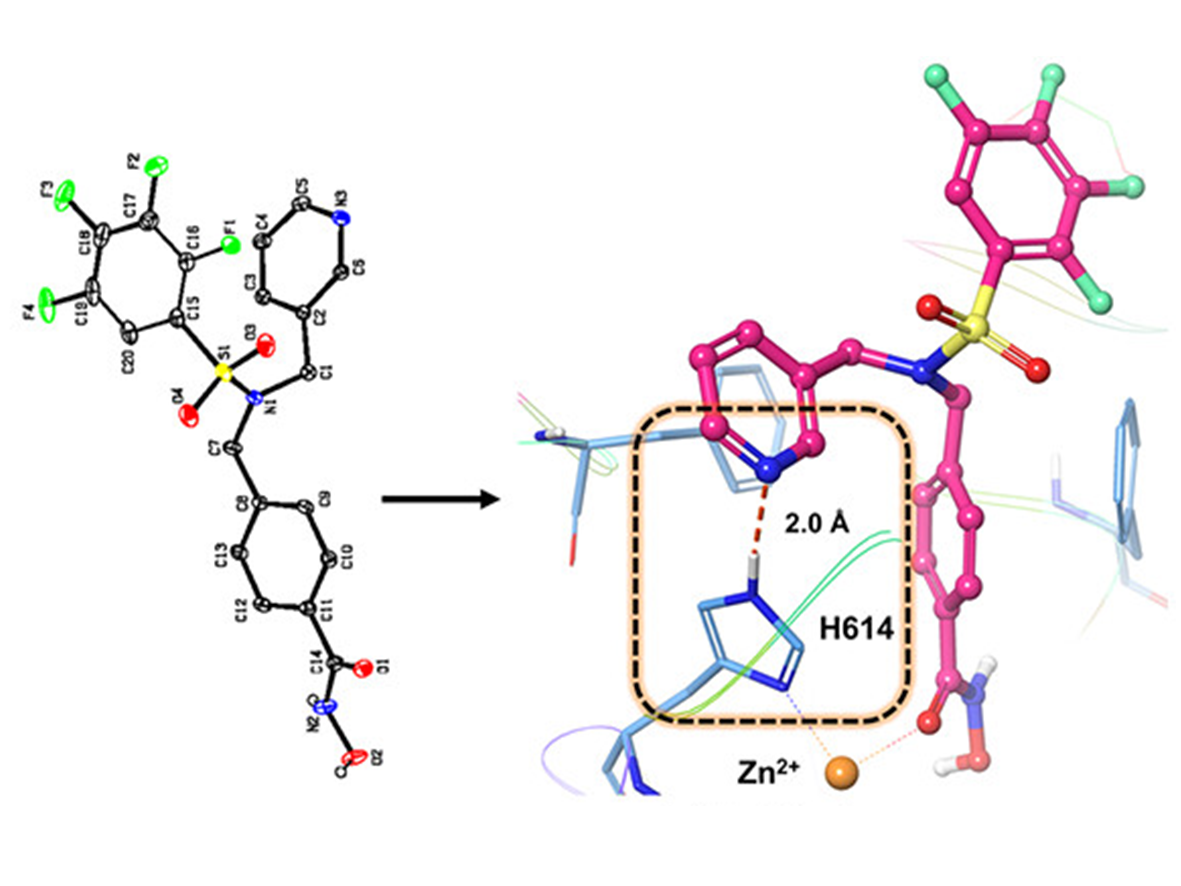
HDAC6 plays an important role in neurological, inflammatory, and other diseases; and thus is an important target for therapeutic intervention. To date, there are no FDA-approved HDAC6-targeting drugs and most pipeline candidates suffer from poor target engagement, inadequate brain penetration, and low tolerability. There are five HDAC6 clinical candidates for the treatment of mostly non-CNS cancers as their pharmacokinetic liabilities exclude them from targeting HDAC6-implicated neurological diseases, urging for the development to address these challenges. They also demonstrate off-target toxicity due to limited selectivity, leading to adverse effects in patients. Selective inhibitors have thus been the focus of development over the past decade, though no selective and potent HDAC6 inhibitor has yet been approved to date.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsFully Homomorphic Encryption
This technology is an optimized version of the Ring-Learning-With-Errors (RLWE) Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) system. This proprietary system maintains encrypted data privacy of communications while still allowing cloud operations to be carried out on the encrypted data, such as Secure Search and Spam-Filter Applications.
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Cybersecurity, Electrical & Computer Engineering, SoftwareResponsive Antiviral Biomaterials
Antibacterial-silica (glass) self-assembled materials that respond to the presence of pathogenic bacteria by releasing drugs on demand when bacteria are present.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemAI-Powered Platform for Better Decision Making
A software platform that leverages statistical inference and machine learning to make more informed decisions.
Read more...Keywords:
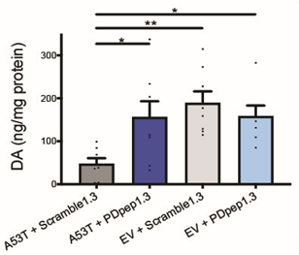
Software, Deep Learning, Data Analytics, Computer Graphics, Machine Learning, CompaniesPeptide Therapeutic for Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a disabling and progressive neurological disorder characterized by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons. Current therapies to replace dopamine are only symptomatic and are associated with considerable complications as the disease progresses. No disease-modifying therapies that slow or stop disease progression are available or likely to emerge soon. With Parkinson’s disease affecting over 6 million people worldwide and being the fastest growing neurological disease, this is a huge unmet need in neurodegeneration.
Read more...Keywords:
TherapeuticsMammalian Membrane Two-Hybrid (MaMTH) Technology: a Novel Protein Interaction and Drug Discovery Tool
Complex multi-protein clusters play vital roles in many aspects of biology. Deregulation of these clusters may lead to several human diseases including cancer, cystic fibrosis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. This technology uses a bait (protein of interest) - prey (candidate molecules) system to detect and identify novel interacting partners in a mammalian genetic system. Dr Stagljar has built upon his initial patented Membrane Yeast Two-Hybrid (MYTH) invention to propose a unique platform to discover new target molecules for research and drug development purposes. This technology provides a new tool to examine membrane proteins in their natural environment of the human cell. It is sensitive enough to detect minor changes upon the introduction of drugs and thus should prove useful in the development of therapeutics, especially for cancer and neurological diseases.
Read more...Keywords:
Screening Platform, Research ToolsLinker-Based Lecithin Microemulsions as Drug Delivery Vehicles
This invention is a novel formulation for biocompatible microemulsions for use as delivery vehicles for active ingredients in transdermal, topical and oral delivery. The formulation is based on five basic ingredients: lecithin (extracted from soybean or other source); a lipophilic additive such as long change alcohol or long chain fatty acid, monoglyceride, or sorbitol ester; a hydrophilic additive containing C6-C9 fatty acids partially saponified; a C8-C20 fatty acid ester; and water. Particular combinations of these ingredients, at specific ratios, yield thermodynamically stable microemulsions capable of increasing the solubility (in isotonic solutions) of hydrophobic drugs such as lidocaine, and alpha-tocopherol acetate by more than 20 fold.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemThe Glucose Meter as a Detection System for Point-of-Care Gene Circuit Diagnostics
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on fluorescent reporter proteins which require multi-well plate reader assays, leaving the technology for all practical purposes stuck in the laboratory. In line with this promise of cell free gene-circuit sensors, we have developed a cheap and accessible detection method at the University of Toronto.
Read more...Keywords:
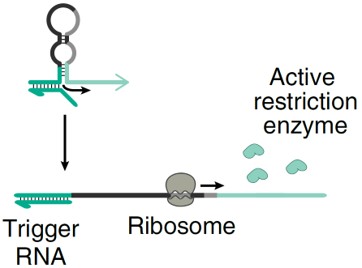
DiagnosticsPoint-of-Care Detection of Infectious Disease Using Restriction-Enzyme-Based Reporters
Point-of-care (POC) testing involves the rapid detection of analytes near patients and enables quick medical decisions that can improve disease diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Cell free systems have been particularly successful as POC diagnostics by utilizing gene-circuit based sensors outside the physiological constraints of cells, which accelerates the product development cycle and enables easy storage, distribution, and use. However, most demonstrations to date rely on optical reporter proteins which require equipment contained in centralized labs and which offer limited multiplexing capabilities. To overcome these limitations, researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a direct gene-circuit/electrode interface that allows point-of-care detection of RNA.
Read more...Keywords:
DiagnosticsTargeted Protein Degradation using Novel E3 Ligases
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is an alternative approach to conventional paradigms (e.g. small molecule inhibitors) that target disease. In this technique, a PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) or a molecular glue is used to initiate the degradation process of the targeted protein. While these two molecular classes are mechanistically distinct, they both enable degradation by recruiting an E3 ligase, an enzyme which enables the transfer of the ubiquitin tag needed for proteasome-mediated degradation. One obstacle to the development of these treatment modalities is that the two E3 ligases largely used with this approach only work with some proteins. Thus, identification of new E3 ligases can increase the disease targeting space of targeted protein degradation therapeutics.
Read more...Keywords:
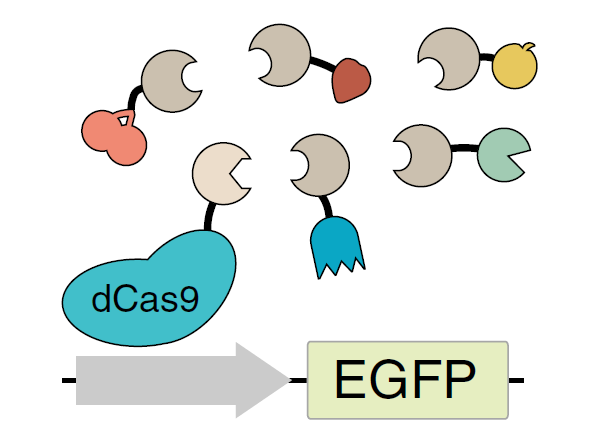
Therapeutics, Research ToolsTunable Activation of Gene Expression for Therapeutic Use
Precisely controlled regulation of gene expression in cells, tissues, and organisms is one of the major challenges in tissue engineering, cell-based therapies, and gene therapy. Controlled gene expression in cells is achieved either by exogenously introducing cDNAs by transfection or viral transduction, or by introducing sequence-specific transcriptional regulators. These regulators include zinc-finger nucleases, transcription activator like effectors (TALEs), or enzymatically inactive Cas9 (dCas9) which are fused to transcriptional activation or repression domains to achieve the desired effect on gene expression. Of these techniques, CRISPR activation (CRISPRa), based on the fusion of inactive Cas9 (dCas9) to various trans-activation domains, is a powerful platform for activating gene expression. However, non-human activators (e.g. VP16) can elicit an immune response necessitating the development of human activators of comparable and tunable efficacy.
Read more...Keywords:
Therapeutics, Research ToolsBiocompatible Microemulsions as Delivery Systems for Poorly Water-Soluble Active Ingredients
Self-Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SMEDDS) is an advanced lipid-based delivery system composed of an isotropic mixture of surfactants and oils that rapidly and spontaneously assemble into microemulsions (5-150 nm) upon exposure to water with a gentle agitation. These features enable enhanced delivery and quick absorption of hydrophobic bioactive compound through gastrointestinal tract and epithelial tissues. SMEDDS are easy to manufacture, offer high loading capacities, and have a long shelf life.
Read more...Keywords:
Drug Delivery SystemNovel Nematicides for Animal Health and Plant Applications
Parasitic nematodes are a major problem in agriculture where their infection of livestock and parasitization of plants are a threat to food security and result in billions of dollars of lost productivity. Several classes of nematicides, compounds that are toxic to nematodes, have been approved and successfully integrated into the food generation process. However, two problems with current nematicides are increasing resistance to their effects and serious concerns with their environmental impact, the latter of which has led to withdrawal of commercially successful nematicides from general use. Researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered two small molecule scaffolds for potential use as nematicides in agricultural applications.
Read more...Keywords:
Small MoleculesScalable Sensing Platform for Point-of-Need Testing
Scalable, portable diagnostics for bacteria detection, molecular diagnostics, and immunoassays through microchip-based optical, electrochemical, ion, pH, and temperature measurements.
Read more...Keywords:
Point-of-Care, Chips, Semiconductors, CompaniesHippoCamera: Digital Memory Augmentation
Hippocamera is a memory augmentation technology that aides in the recall and storage of memories. The technology features novel methods to tag and replay recorded moments to promote rich reliving and storage of experiences.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cameras, Communications, Companies, Digital Media, Health & Related Life Sciences, Image & Video Processing, Mobile Apps, Neurological Disorders, Smartphones, SoftwareJALI: Automated 3D Lip Synchronization and Facial Animation
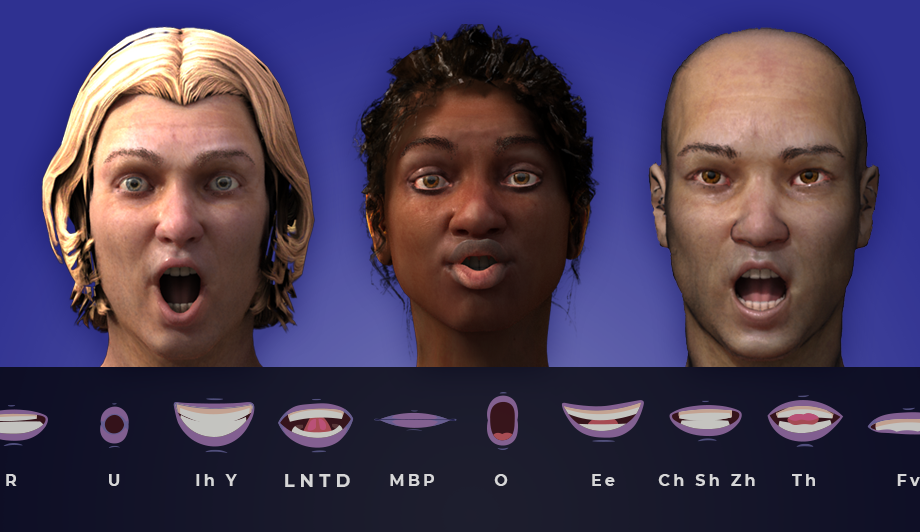
JALI provides products and services for the complete automation of high-end lip sync and facial animation for ultimate animator directorial control.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Animation, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Companies, Computer Graphics, SoftwareRhea: Digital Wellness Platform for Personalized Brain Rehabilitation
Rhea is a rehabilitation platform and startup grounded in science that active recovery to heal and care for the brain.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Companies, Digital Media, Health & Related Life Sciences, Mobile Apps, Neurological Disorders, Sensory Systems & Rehabilitation, Smartphones, Software, Wearable TechPhenoTips: Software for Patient Phenotyping
PhenoTips is a B2B digital health spinout from U of T and SickKids, helping healthcare systems prepare for a future when genetics is a critical part of every patient's routine care. Healthcare workers use PhenoTips through their existing EHRs to manage critical data for genomic medicine,
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Diagnostics, Patient Care, SoftwareODAIA: AI-Driven Customer Journey Intelligence
ODAIA is business intelligence software that enables organizations to understand, predict, and optimize their customer's journeys. The technology leverages AI to facilitate the exploration, analysis, summarization, and optimization of a customer's journey, from awareness to purchase.
Read more...Keywords:
Data Analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Software, Companies, Research ToolsDeep Learning Performance and Energy Optimization Techniques
This opportunity is a portfolio of hardware and software techniques that seamlessly accelerate AI/ML applications, while saving on-chip and off-chip memory, bandwidth, and processing power. These compute and compression methods have been shown to deliver a 3x boost in processing speed with 2x-4x increase in storage capabilities (up to 10x for natural language processing).
Read more...Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Chips, Companies, Computer Hardware, Deep Learning, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Smart Cities, SoftwareCryosparc: Accelerated Protein Structure Determination from Cryo-EM
High-performance software solutions and advanced algorithms for cryo-EM data processing.
Read more...Keywords:
3D Imaging, Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Companies, Drug Discovery, Machine Learning, Research Tools, SoftwareAutoscribe: AI-Powered Voice Assistant for Clinicians
AutoScribe uses hands-free speech recognition and Artificial Intelligence to help reduce time consuming manual clinical documentation, freeing clinicians to place their focus where it should be – on their patients.
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Communications, Companies, Deep Learning, Health & Related Life Sciences, Human-Computer Interaction, Machine Learning, Patient Care, Point-of-Care, SoftwareAdaptive Neural Implant for Modulation and Observation (ANIMO)
Invasive and non-invasive hardware and software for vital signs monitoring
Read more...Keywords:
Advanced Health Technologies, Wearable Tech, Machine Learning, Battery, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Circuit design, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Medical DevicesSelective Enhancement of Electrical Nerve Excitability
Treatment of overactive bladder and other disorders via non-invasive electrical neurostimulation.
Read more...Keywords:
Companies, Medical Devices, Medical Implants & Prosthetics, Neurological Disorders, Advanced Health Technologies, SoftwareQuantum-Safe Encryption and Communication
Quantum-proof cybersecurity products and enabling technologies for the Quantum Internet. These technologies offer quantum-safe communication products ready for today's infrastructure, while building key components of the Quantum Internet, including Quantum Repeaters, Quantum Communication Protocols, and Quantum Network Simulators.
Read more...Keywords:
Communications, Companies, Computer Hardware, Cybersecurity, Electrical & Computer EngineeringCentivizer: An Interactive, Modular Approach to Dementia Care
Centivizer is a modular system that physically, cognitively, and socially stimulates individuals with dementia by providing self-initiated, reward-based activities that can be used 24/7 without needing caregiver support.
Read more...